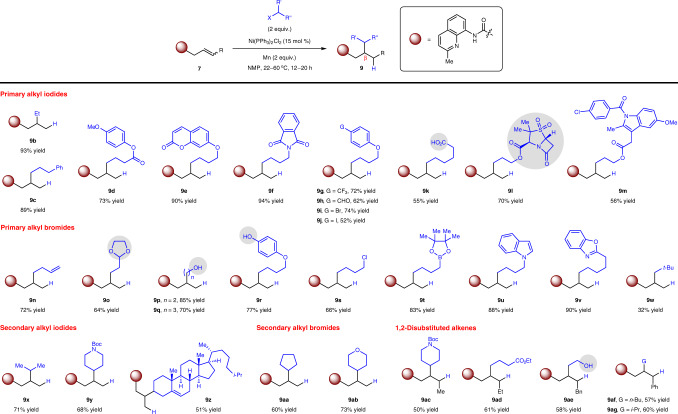
Fig. 3. The range of products accessible by reductive olefin hydroalkylation.
The protocol is compatible with both primary and secondary alkyl halides bearing Brønsted/Lewis acidic and basic functionalities, including those derived from complex bioactive molecules. Both mono- and 1,2-disubstituted alkenyl amides are tolerated in the catalytic system. For 9w, the reaction was conducted with neopentyl bromide (3 equiv.) and isopropyl bromide (1.2 equiv.) using NiI2 as the catalyst. For 9ac and 9af, reactions were conducted using iodides (X = I). For 9ad, 9ae, and 9ag, reactions were conducted using bromides (X = Br). For 9j, ~20% of an inseparable hydrodeiodination side product was detected. For 9m, ~3% of an inseparable self-coupling side product of iodide substrate was detected. 9g, 9i, 9u, 9ab, and 9af were obtained as 88:12, 93:7, 92:8, 90:10, and 91:9 regioisomeric mixtures, respectively. 9l and 9z were obtained as 5:1 and 1:1 diastereomeric mixtures, respectively. Regioisomeric and diastereomeric ratios were determined by 1H NMR analysis. Yields are for isolated and purified products. R, functional group; X, halide; NMP, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone; Boc, tert-butoxycarbonyl.