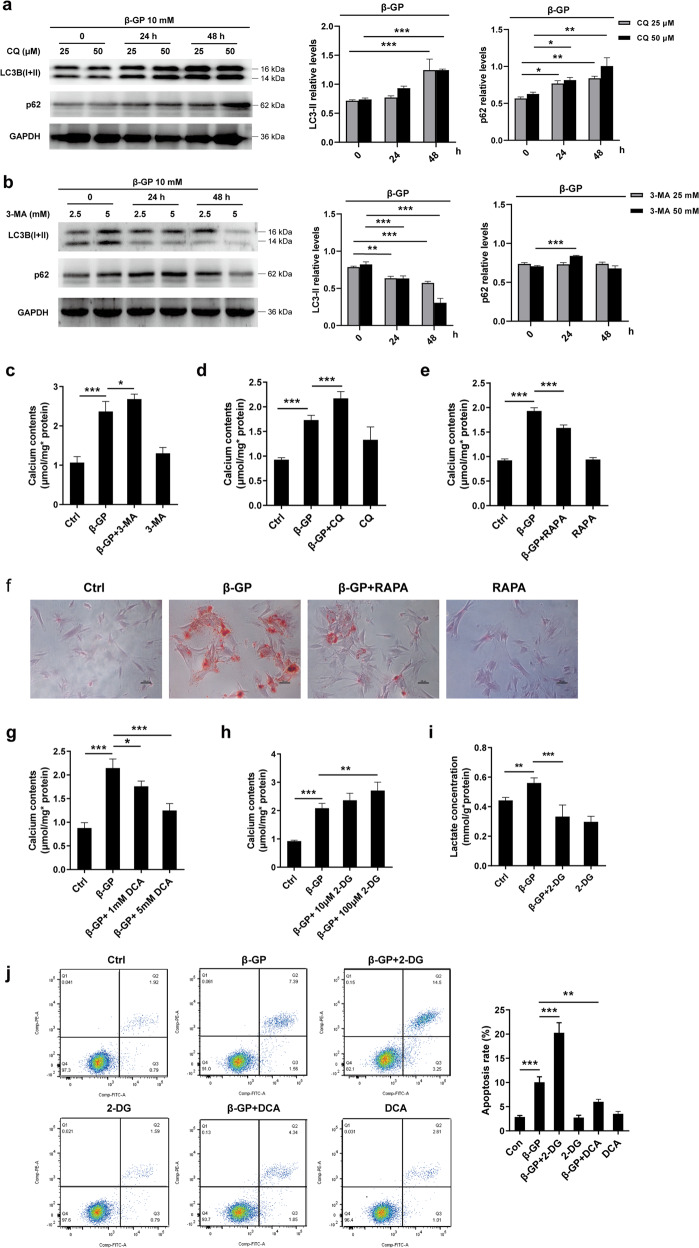
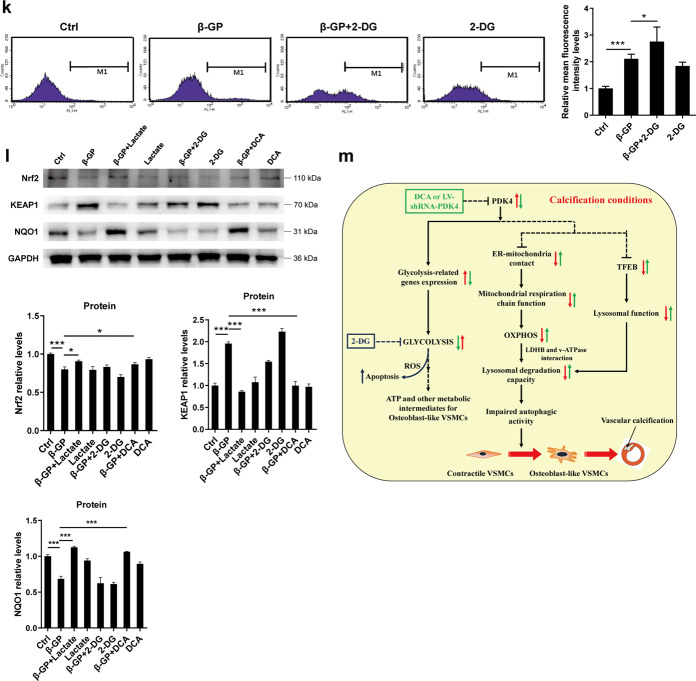
Fig. 7. Targeting autophagic-lysosomal function and glucose metabolism affects calcium deposition in VSMCs.
a, b Cells were treated with CQ or 3-MA at the indicated concentrations plus β-GP for 24 h, and the protein expression of LC3-II and p62 was determined by western blotting. N = 3 independent experiments. c, d Cells were incubated with 10 mM β-GP in the absence or presence of CQ or 3-MA for 14 days. Then, the calcium content was measured. N = 5 independent experiments. e, f VSMCs were treated with 10 mM β-GP in the absence or presence of rapamycin for 14 days, and the calcium deposition was visualized by a calcium assay kit and Alizarin red S staining at the light microscopic level (original magnification, ×100; Scale bars = 100 μm). g Cells were incubated with 10 mM β-GP in the absence or presence of various DCA concentrations for 14 days, and the degree of calcium deposition was detected by a calcium assay kit. N = 5 independent experiments. h Cells were exposed to 10 mM β-GP in the absence or presence of various 2-DG concentrations for 14 days, and the calcium deposition was quantitatively analysed using a calcium assay kit. N = 5 independent experiments. i Lactate production was measured using a lactate assay kit. N = 5 independent experiments. j Apoptotic cells were measured by flow cytometry with cells stained with Annexin V-FITC in combination with PI. N = 3 independent experiments. k VSMCs were treated with 10 mM β-GP in the presence or absence of 100 μM 2-DG for 72 h, and ROS production was measured by flow cytometry. N = 3 independent experiments. l Protein expression of Nrf2, Keap1 and NQO1 was detected by western blotting. N = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. m Proposed mechanisms regarding the effects of PDK4 on vascular calcification: Disrupted ER-mitochondria interactions caused by upregulation of PDK4 contributes to impaired mitochondrial respiration, which decreases lysosomal function via inhibition of LDHB and v-ATPase A1 interaction. Meanwhile, PDK4 inhibits lysosomal function via inhibition of the nuclear translocation of TFEB. These consequences collaborate and contribute to impaired autophagic activity, which has been implicated in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification. In addition, PDK4 drives metabolic reprogramming of VSMCs, with a higher rate of glycolysis under calcification conditions; while inhibition of glycolysis promotes apoptosis in VSMCs.