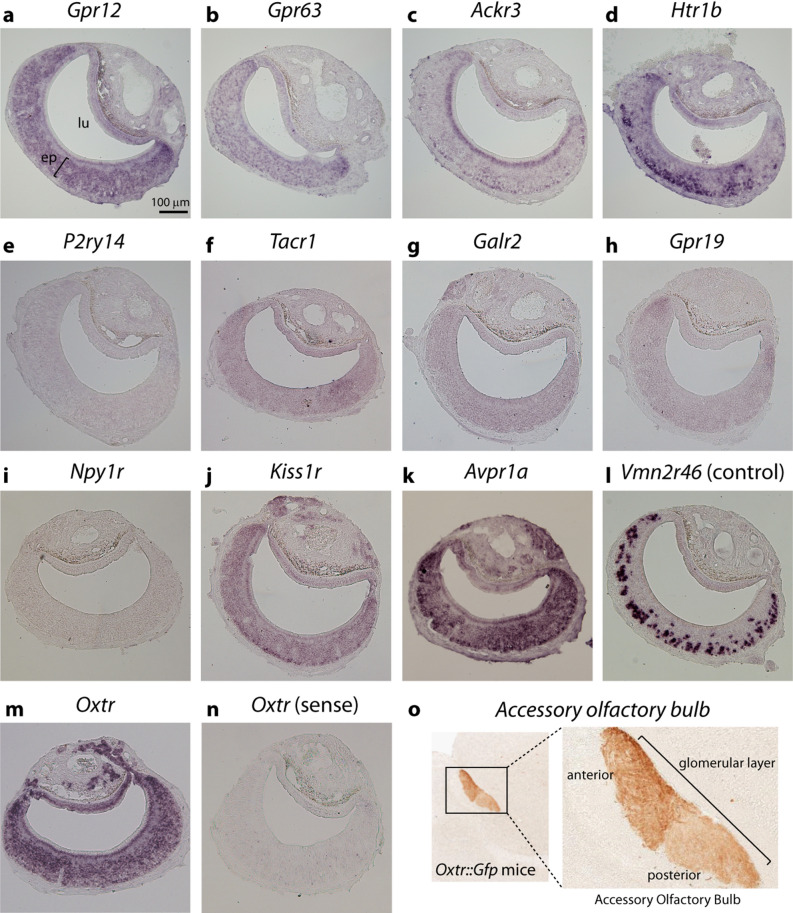
Figure 2.
In situ hybridization for candidate hormone receptor genes in the vomeronasal organ of adult virgin male mice. (a–n) Each panel shows chromogenic in situ hybridization staining (purple) on VNO coronal sections with probes for genes Gpr12 (a), Gpr63 (b), Ackr3 (c), Htr1b (d), P2ry14 (e), Tacr1 (f), Galr2 (g), Gpr19 (h), Npy1r (i), Kiss1r (j), Avpr1a (k), and Oxtr (m). Positive control (l) is staining with probe for V2R vomeronasal receptor gene Vmn2r46, expected to be expressed in a large set of cells in the VNO's basal zone. For the oxytocin receptor gene Oxtr, staining obtained with a control sense probe is shown for comparison (n). ep, vomeronasal sensory epithelium; lu, vomeronasal organ lumen. Bar is 100 μm. (o) Glomerular layer of the accessory olfactory bulb from Oxtr::Gfp transgenic mice where GFP is under the control of the Oxtr gene promoter (GENSAT Project database56). Immunostaining for GFP is shown in brown. Higher magnification image on the right shows anterior and posterior divisions of the bulb.