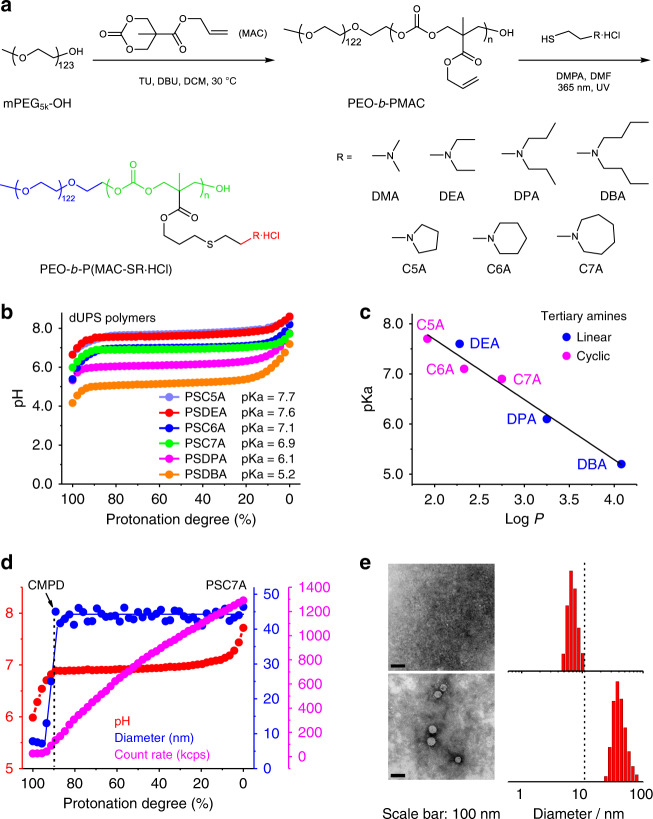
Fig. 1. Micellization-induced ultra-pH sensitivity of degradable ultra-pH sensitive (dUPS) polymers.
a Synthesis of PEO-b-P(MAC-SR·HCl) (abbreviated as PSR) by ring-opening polymerization and thiol-ene reactions. The final copolymers consist of a hydrophilic PEO segment (blue), a degradable polycarbonate backbone (green), and ionizable tertiary amines lending pH sensitivity (red). b dUPS polymers display ultra-pH sensitivity and strong buffer capacity at their relative pKa. PSDMA titration is presented separately in Supplementary Fig. 10. c pKa values are inversely correlated with the log P of the repeating unit of the P(MAC-SR) segment (neutral/deprotonated state). d Number-weighted hydrodynamic diameters and light scattering count rates as a function of protonation degree during the PSC7A titration. CMPD: critical micellization protonation degree. e TEM images and corresponding number-weighted hydrodynamic diameter distributions by dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis of PSC7A in 150 mM NaCl solution at 95% and 85% protonation degrees, above and below CMPD. Scale bar: 100 nm. TEM measurements of PSC7A polymer solutions at 85% and 95% protonation degrees were repeated three times independently with similar results, and one representative image from each group was shown.