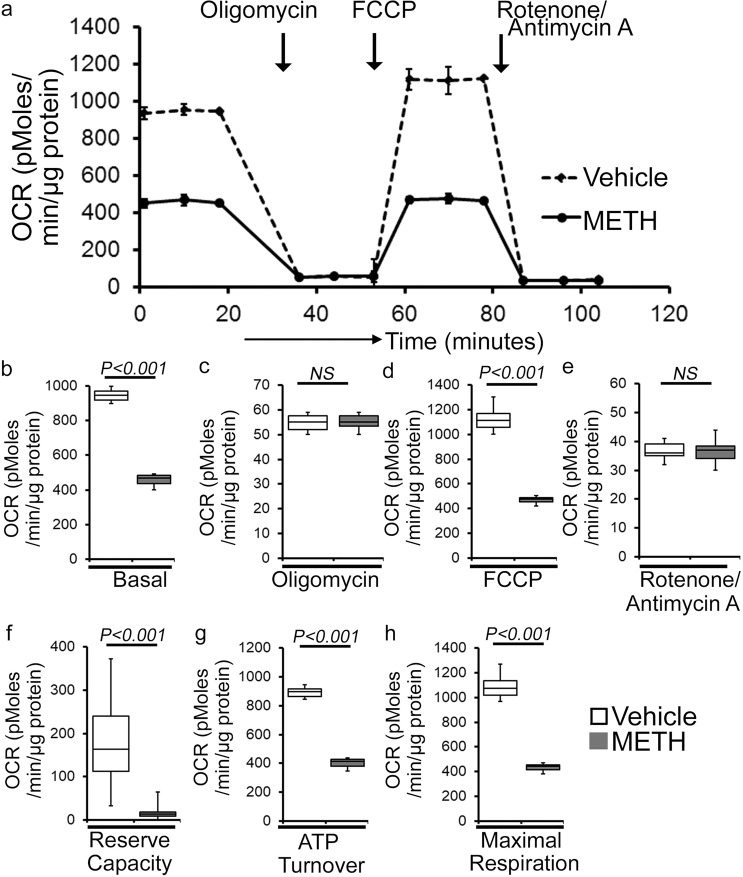
Fig. 8. METH treatment induces impaired mitochondrial bioenergetics in the heart.
a Summary traces of mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate (OCR) profiles as measured in isolated mitochondria from the hearts of vehicle- and METH-treated mice. The black arrow indicates the sequential addition of oligomycin (1 μmol/L), FCCP (carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone) (4 μmol/L), and rotenone (0.5 μmol/L) plus antimycin A (0.5 μmol/L). OCR profiles are expressed as pmol O2/[min*μg protein], and each point represents average OCR values from five individual mouse cardiac mitochondria per group. b–e Bar graphs represent OCR under b baseline and with the addition of c oligomycin, d FCCP, and e rotenone plus antimycin A. f–h Key parameters of mitochondrial bioenergetics, including f reserve capacity, g ATP turnover, and h maximal respiration were significantly decreased in METH-treated mice compared to vehicle-treated mice. Boxes depict interquartile ranges, lines represent medians, and whiskers represent ranges. P values were determined using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. P < 0.05 between groups was considered statistically significant. Veh vehicle, METH methamphetamine.