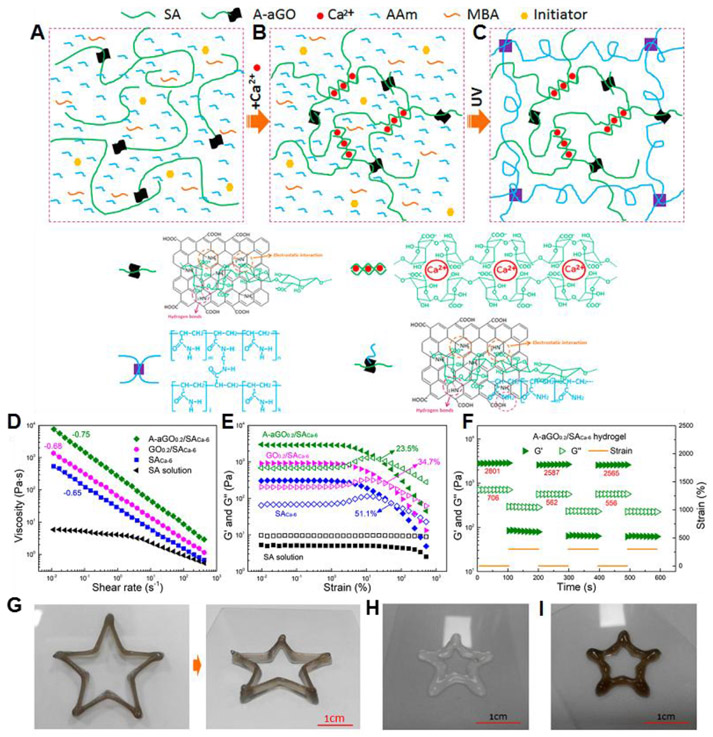
Figure 19.
(A-C) Schematic diagrams for fabrication of the A-aGO/SA/PAAm nanocomposite hydrogel: (A) Homogeneous aqueous solution of SA, A-aGO, acrylamide (AAm), N,N’-methylene bisacrylamide (MBA), and photoinitiator. (B) Ca2+ ions inducing ionic association of SA chains. (C) UV exposure resulting in the final A-aGO/SA/PAAm nanocomposite hydrogel. (D) Apparent viscosity as a function of shear rate for the A-aGO0.2/SACa-6 and SACa-6 hydrogels as well as the SA solution without Ca2+ ions. (E) Storage modulus G′ and loss modulus G″ as a function of oscillation strain at an angular frequency of 1 Hz for the A-aGO0.2/SACa-6 and SACa-6 hydrogels as well as the SA solution without Ca2+ ions. (F) Changes of G′ and G″ with time at alternant oscillation strains of 2% and 300% and at an angular frequency of 1 Hz for the A-aGO0.2/SACa-6 hydrogel, where the red numbers represent the average modulus at the oscillation strain of 2%. (G) Hollow pentagon printed from the A-aGO0.2/SACa-6/AAm hydrogel bioinks (15 layers) viewed from the top and side. 3D printed hollow pentagon patterns from (H) the SACa-6/AAm hydrogel and (I) the GO0.2/SACa-6/AAm hydrogel inks, respectively. Reprinted with permission from ref 352. Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society.