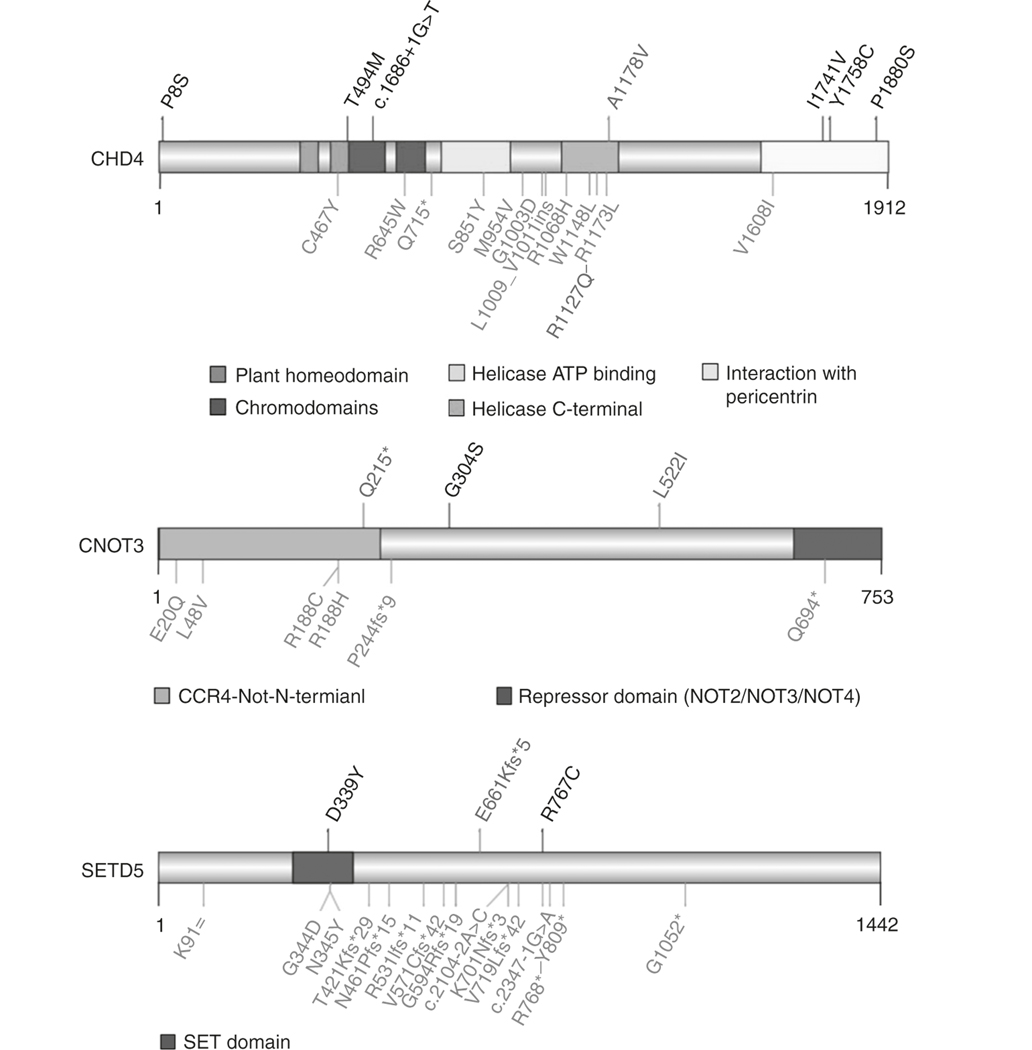
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of domains of the proteins encoded by CHD4, CNOT3, and SETD5 and the location of the rare variants identified in individuals with either moyamoya angiopathy (MMA) or developmental disorders.
Above the protein schematics are the location of rare de novo variants (red) and variants (black) identified in singleton cases in the MMA cohort. Below the protein schematics are variants identified in children with intellectual disability, congenital heart defects, or developmental disorders (blue).11,12 The red variant in the CHD4 schematic was identified in three unrelated patients, including the patient described with intellectual disability and moyamoya disease11 (CHD4: NP_001264.2, CNOT3: NP_055331.1, SETD5: NP_001073986.1). ATP adenosine triphosphate.