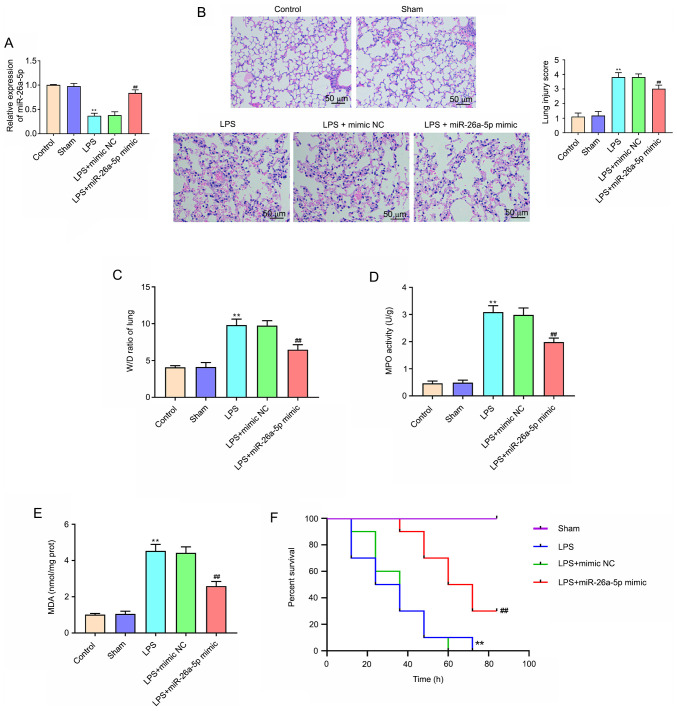
Figure 1.
Overexpression of miR-26a-5p alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Mice in each group underwent intraperitoneal injection of miR-26a-5p mimics or NC mimics (20 mg/kg) 24 h before treatment with 5 mg/kg LPS. Mice were sacrificed after LPS administration for 24 h and then lung tissues were collected for analysis (except the survival experiment). (A) The expression of miR-26a-5p in lung tissues was detected by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (n=5/group). (B) Pathological changes in the lung tissues observed by H&E staining (×100, magnification) (n=5/group). (C) The lung W/D weight ratio was assessed among the experimental groups (n=6/group). The activity of (D) MPO and the content of (E) MDA in lung tissues were detected using the corresponding test kits (n=6/group). (F) The survival rates were observed during 84 h following LPS treatment (n=10/group). Data were presented as the mean ± SD. **P<0.01 vs. Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs. LPS + mimic NC group. miR, microRNA; NC, negative control; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; W/D, weight/dry; MDA, malondialdehyde; MPO, myeloperoxidase.