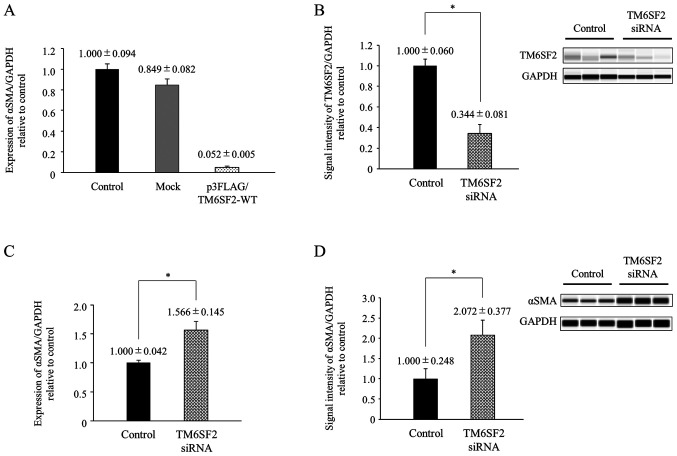
Figure 1.
TM6SF2 regulates αSMA expression in LX-2 cells. (A) The cloned TM6SF2 expression plasmid (p3FLAG/TM6SF2-WT) and empty vector (Mock) were transiently transfected into LX-2 cells followed by 24 h of incubation. Intracellular αSMA expressions were measured by quantitative PCR. The expression of GAPDH served as a control. Experiments were performed in triplicate wells. (B) Non-treated and TM6SF2 knocked-down LX-2 lysates were transferred onto a automated capillary western blot analysis. Anti-TM6SF2 antibody or anti-GAPDH antibody were applied, followed by anti-rabbit immunoglobulin. Signal intensity was corrected by GAPDH and is shown in the bar graph. (C) Intracellular αSMA expression, measured by quantitative PCR, was compared in non-treated and TM6SF2 knocked-down LX-2 cells. GAPDH expression was used as a control. Experiments were performed in triplicate wells. (D) Non-treated and TM6SF2 knocked-down LX-2 lysates were transferred onto an automated capillary western blotting system. Anti-αSMA antibody or anti-GAPDH antibody were applied, followed by anti-rabbit immunoglobulin. Signal intensities were corrected by GAPDH and are presented in the bar graph. Experiments were performed in duplicate wells. *P<0.05. TM6SF2, transmembrane 6 superfamily 2; TGFβ1, transforming growth factor β1; αSMA, α-smooth muscle actin; si, small interfering.