Figure 1.
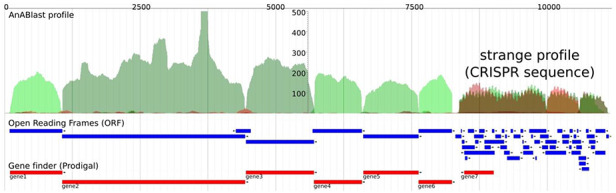
AnABlast profile of a genomic region that contains a CRISPR sequence (CP001172.2: 1 057 766–1 068 943). The profile shows accumulations of low-score sequence alignments between the genomic region and database protein sequences taken as protein-coding signals (called protomotifs). Green peaks correspond to accumulations in the forward strand, and red peaks correspond to accumulations in the reverse strand. Blue annotations represent ORFs, and red annotations are protein-coding genes predicted by a prokaryotic gene finder. Peaks above a height threshold, matching with predicted ORFs, stand for known protein-coding genes which are CRISPR-associated genes (cas) in this case (green peaks). But the strange profile at the end, which presents a series of both short peaks and ORFs in the two strands, including a putative gene in the reverse strand (gene7), is in fact a CRISPR sequence consisting of repeats (peaks) and spacers (valleys).
