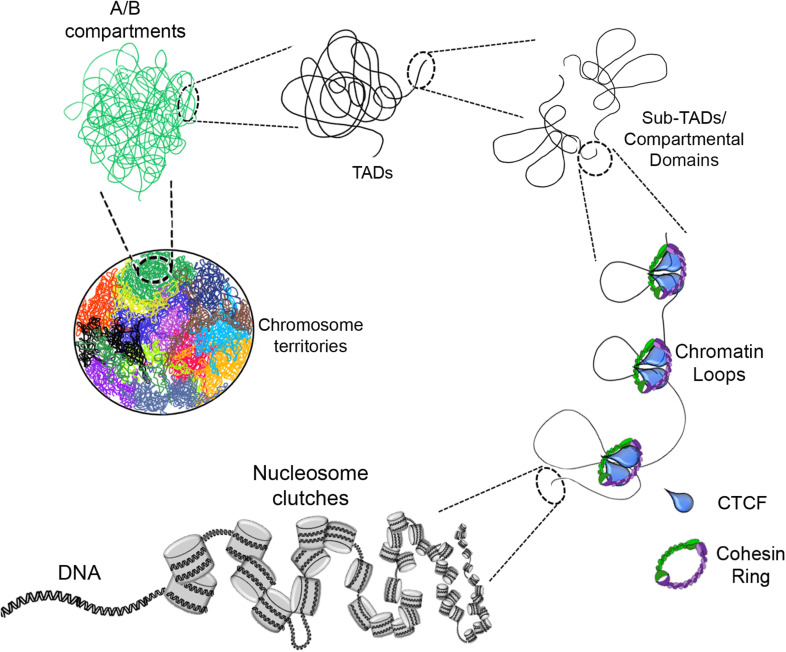
FIGURE 1.
Eukaryotic chromatin organization. The DNA interacts with histone octamers and aggregates forming nucleosome clutches. In the next level of compaction are the chromatin loops which are formed by loop extrusion and in a greater extent stabilized by CTCF and the cohesin ring. Chromatin loops are the base of compartmental domains, sub-TADs and TADs which range from ten of kb to Mb structures with delimited boundaries and high-rate interactions inside of these domains. A/B compartments is the next level, where can be determined by gene content, epigenetic marks, DNase hypersensitivity and nuclear localization. Finally, there are the chromosome territories which are the localization of each chromosome inside the nucleus (each color represents a different chromosome).