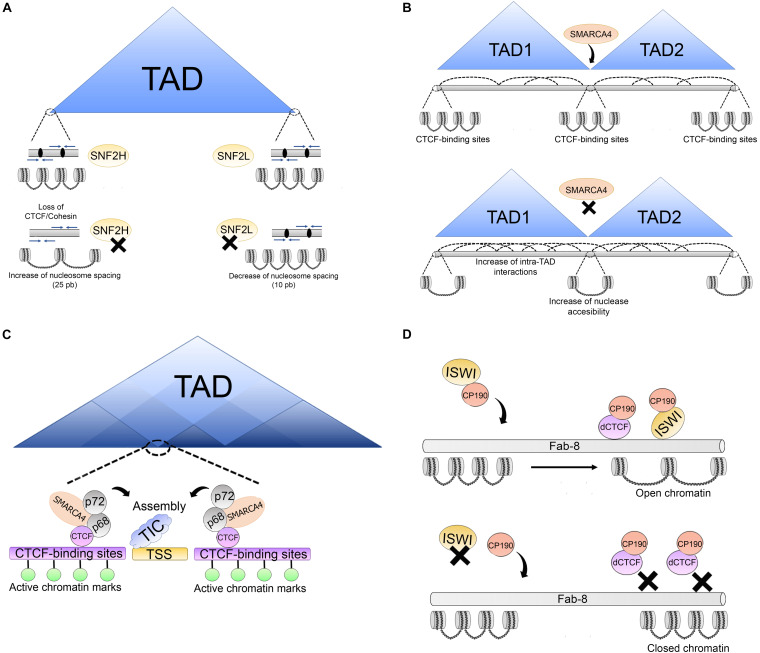
FIGURE 5.
Association of architectural proteins with CRCs in vertebrates. (A) SNF2H and SNF2L are involved in the regulation of nucleosomes at TAD boundaries which are enriched with convergent CTCF binding motifs (blue arrows), CTCF binds and retains the cohesion complex (black ovals). After SNF2H depletion, nucleosome spacing increases over 25 bp promoting loss of CTCF/cohesin complexes. SNF2L depletion alters nucleosome organization of nucleosomes surrounding the CTCF sites and decreases nucleosome spacing over 10 bp. (B) SMARCA4 is a regulator of higher order chromatin structure. Upon SMARCA4 knockdown, weakening of TAD boundaries is triggered increasing intra-TAD and inter-TAD interactions. Additionally, this promotes changes in nucleosome positioning around the CTCF-binding sites, leading to an increase in nuclease accessibility around the CTCF-binding sites. (C) Association between SMARCA4/p68/p72 complex and CTCF. This complex is located on CTCF-binding sites around some TSS enriched with active histone marks. The p66/p72 complex is involved in promoting the assembly of transcription initiation complexes (TIC). The association between SMARCA4/p68/p72 suggests that this complex may be an important CTCF co-factor in chromatin architecture maintenance at some sites which is important for correct transcriptional output. (D) Association of architectural proteins with CRCs in Drosophila. At some insulator sites, as Fab-8, ISWI CRCs (which are directed to these sites by CP190) promote an open chromatin structure at dCTCF-binding sites for insulator function. ISWI depletion alters nucleosome phasing at these sites triggering a closed chromatin state, impairing dCTCF binding and insulator function.