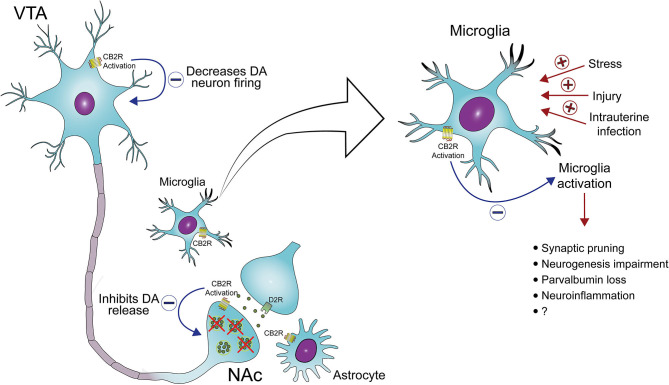
Figure 1.
CB2 receptors as a target to treat midbrain dopamine system dysregulation and neuroinflammation in schizophrenia. The activation of CB2 receptors located in the cell body of ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine (DA) neurons and the terminal of these neurons in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) decreases DA neuron firing and DA release, respectively. In addition, the activation of CB2 receptors in microglia decreases the release of pro-inflammatory mediators and, possibly, microglia-mediated neurotoxicity. Several risk factors for schizophrenia, such as stress and maternal immune activation, lead to microglia activation, which has been associated with abnormal synaptic pruning, neurogenesis impairment, deficits in parvalbumin expression, and neuroinflammation, all common findings in schizophrenia.