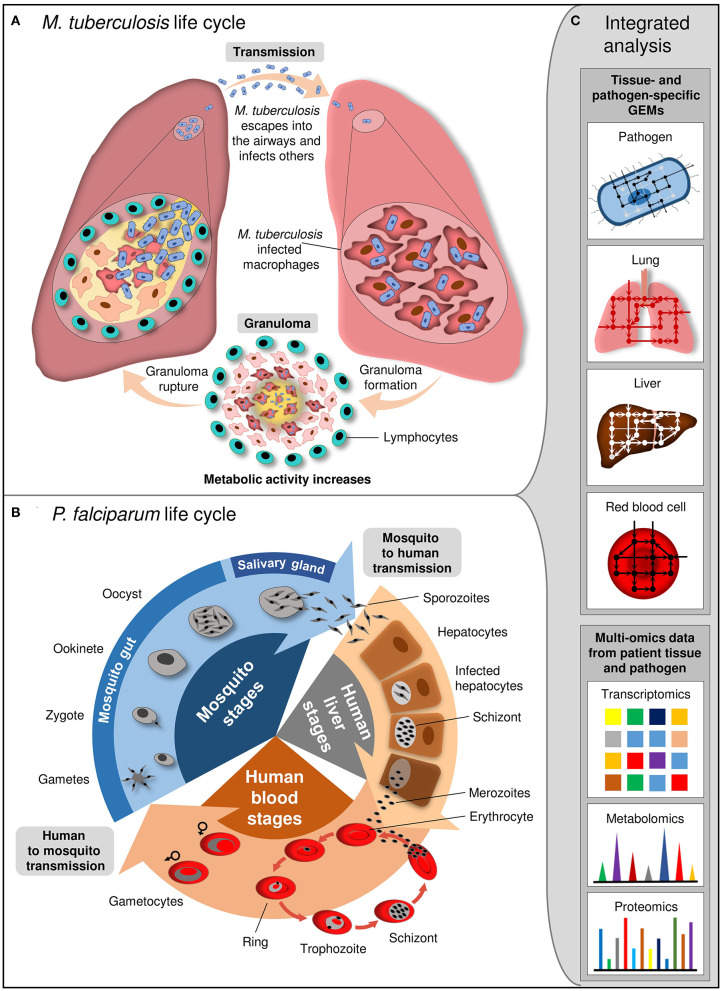
Figure 3.
Life cycle of M. tuberculosis and P. falciparum and integrated analysis at system level. (A) M. tuberculosis is transmitted by aerosol. Inhaled pathogen reaches the alveoli of the lung and grows inside the alveolar macrophages. Granuloma, where M. tuberculosis kills the macrophages and escapes from the cell for division, is formed. Subsequent to maturation, granuloma ruptures and releases M. tuberculosis into the airways. (B) P. falciparum life cycle involves the different stages in female Anopheles mosquito and human. Mosquito transmits sporozoites into the human. They infect hepatocytes and mature into schizonts which release merozoites. Merozoites invade erythrocytes and resulted in release of newly multiplied merozoites by erythrocytes destruction. Some merozoites differentiate into gametocytes which are taken up from host by mosquito. Gametocytes develop into sporozoites within mosquito. (C) Integrated analysis of tissue- and pathogen-specific GEMs with the high-throughput multi-omics data provides insight into the cellular and interaction mechanisms between the pathogen and host tissue at different stage of infection.