Fig 2.
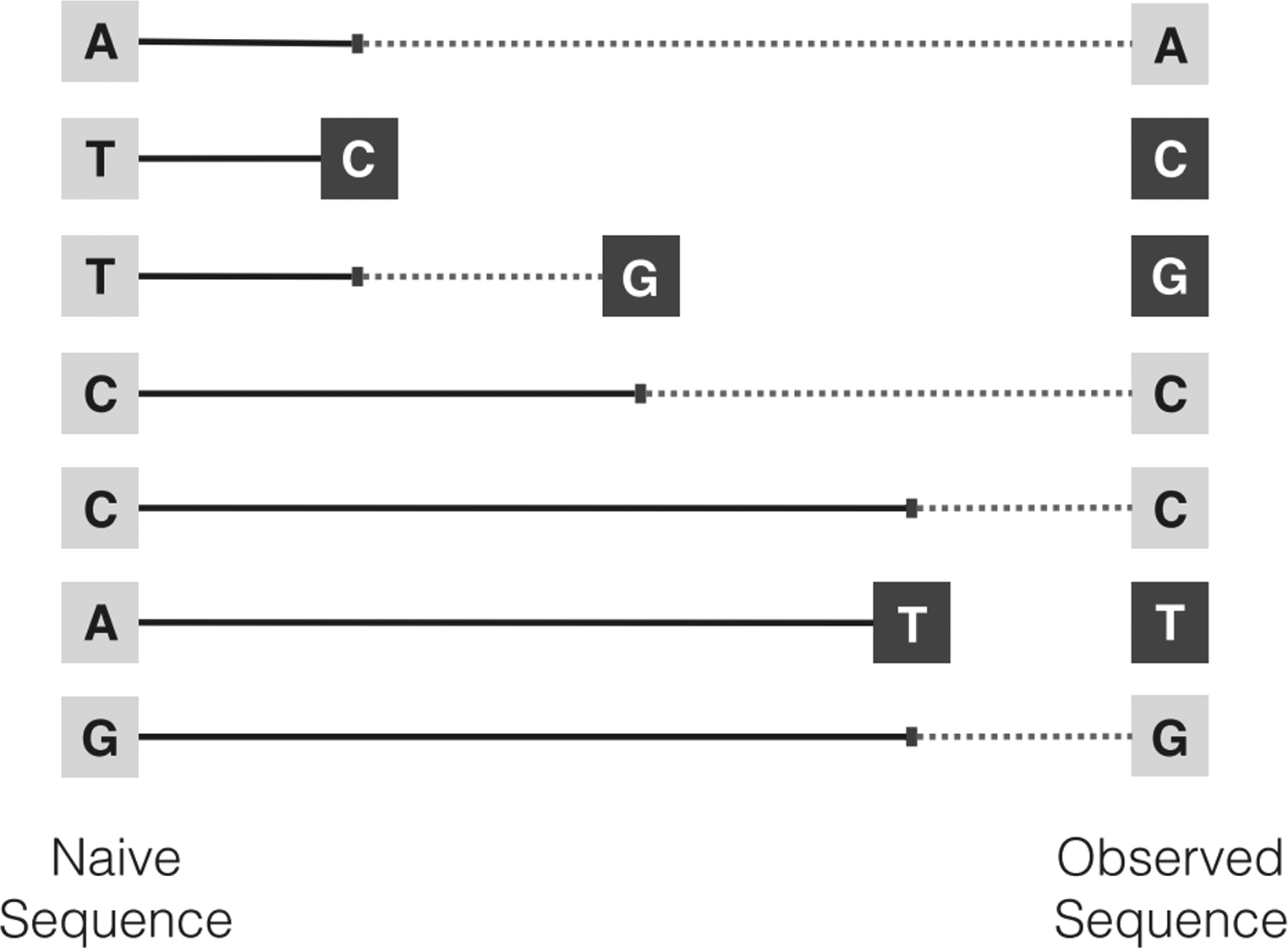
Survival analysis for BCR sequences, where the positions that have not mutated are indicated by light gray squares and those that have mutated are indicated by dark gray squares. In a context-dependent mutation model, a mutation event can change the mutation rates of other positions. Suppose the hazard (i.e. mutation) rate of a position depends on the position’s two neighboring bases. Then, for example, when the T in the third position mutates to a G, the hazard rate for C in the fourth position changes from the original TCC motif to the GCC motif. Changes in the motif at a potential mutating position, and thus its hazard rate, are indicated by a change from solid to dashed lines.
