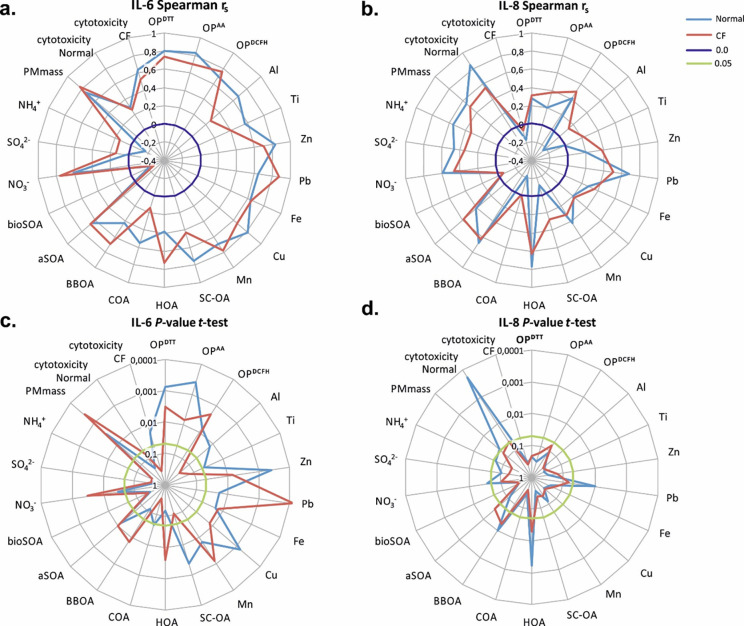
Fig 4. Association between cellular responses upon exposure to PM and chemical parameters of the PM.
(a) and (b) non parametric correlation (Spearman rs), (c) and (d) Student’s t-test p-values of rs. The correlation was derived from the release of interleukins (IL-6 and IL-8) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in normal and cystic fibrosis (CF) HBE after exposure to PM filter extracts. OPDTT, OPAA and OPDCFH refer to the oxidative potential of PM determined using the three acellular assays: dithiothreitol (DTT), ascorbic acid (AA) and 2’7’-dichlorofluorescin (DCFH). The following chemical components of PM are included (see Methods): exhaust (hydrocarbon-like OA–HOA) and non-exhaust (organic sulfur-containing OA—SCOA, metals: Cu, Fe, Mn) primary traffic emissions, cooking emissions (COA), primary biomass burning emissions (organic: BBOA, metals: Zn, Pb), crustal material (Ti, Al), anthropogenic SOA (aSOA), biogenic SOA (bioSOA) and secondary inorganic aerosol (SIA, NH4+, NO3-, SO42-).