Fig. 5. Increased RA signaling inhibits SOX9 expression and fracture healing.
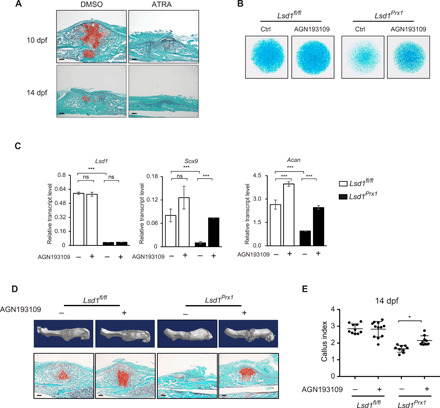
(A) Safranin O staining was performed to detect cartilage formation at 10 and 14 dpf in ATRA-treated (15 mg/kg, daily) or vehicle control-treated mice. n = 3 mice per group. Scale bars, 100 μm. (B) Alcian blue staining of micromass culture using periosteal cells isolated from 4-week-old Lsd1Prx1 and control mice treated with AGN193109 or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). n = 3. (C) RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of Lsd1, Sox9, and Acan in AGN193109- or DMSO-treated micromass samples. Scale bars, 100 μm. ns, not significant, ***P < 0.001. (D) Reconstruction of μCT data reflected hard bony callus formation and Safranin O staining that showed cartilage formation of Lsd1Prx1 and control mice treated with AGN193109 or DMSO. (E) CI calculated from radiographic data showed the callus formation at 14 dpf of Lsd1Prx1 and control mice treated with AGN193109 or DMSO. N ≥ 9 for each group. Data are presented as means ± SD; unpaired t test, *P < 0.05.
