Fig. 7. C28 impedes tumor growth of BC mouse models.
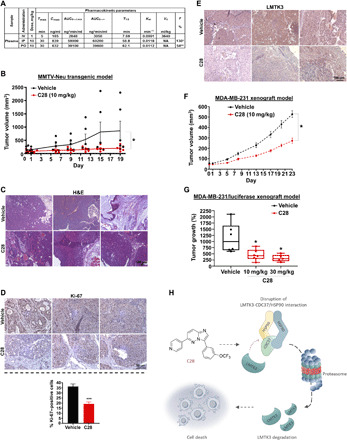
(A) PK parameters of C28 following a single intravenous (IV), intraperitoneal (IP), or oral (PO) dose administration in male BALB/c mice (n = 4 per time point). *, based on 1 mg/kg intravenous group. **, based on 5 mg/kg intravenous group. Intravenous dose of 5 mg/kg was lethal for some mice, and therefore, the dose was decreased to 1 mg/kg. (B) Tumor growth in vehicle- and C28-treated groups (n = 6 each) of MMTV-Neu transgenic mice. Unpaired t test was performed using Prism 8. Results are expressed as means ± SEM; *P < 0.05. (C) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of tumor sections from MMTV-Neu animals treated with vehicle or C28 (10 mg/kg). Original magnification, ×10. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Representative IHC images of Ki-67 expression in tumor sections from MMTV-Neu animals treated with vehicle or C28 (10 mg/kg). Original magnification, ×40. Scale bar, 50 μm. The percentage of Ki-67–positive cells versus the total number of cells is shown. Data represent the average of four vehicle and five C28-treated samples. Results are expressed as means ± SEM; ***P < 0.001. (E) Representative IHC of LMTK3 expression in tumor sections from MMTV-Neu animals treated with vehicle or C28 (10 mg/kg). Original magnification, ×20. Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) Tumor growth in vehicle- and C28-treated groups (n = 14 each) of MDA-MB-231 mice xenografts. (G) Box-and-whisker plots comparing vehicle (n = 6)–treated and C28-treated (10 mg/kg, n = 6 and 30 mg/kg, n = 5) groups of MDA-MB-231–luciferase mice xenografts groups at day 21. Unpaired t test was performed using Prism 8. Results are expressed as means ± SEM; *P < 0.05. (H) Schematic model depicting the proposed mechanism of action of C28 inhibitor.
