Fig. 7. Schematic representation of the HA crystallization pathways.
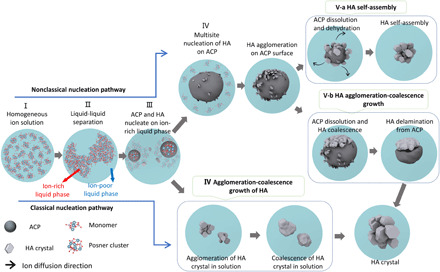
HA crystal formation can be divided into classical and nonclassical nucleation pathways. For the nonclassical nucleation pathway, there are five stages: homogeneous ions in solution (stage I), liquid-liquid separation forming ion-poor and ion-rich liquid phases (stage II), the formation of ACP and HA in ion-rich liquid phase (stage III), multisite heterogeneous nucleation of HA on the surface of ACP (stage IV), and ACP-HA phase transformation (stage V). Stage V can proceed by two different scenarios: One is HA growth only by ACP dissolution–HA reprecipitation followed by HA self-assembly (stage V-a), and the other one is the ACP dissolution–HA reprecipitation followed by HA growth via agglomeration and coalescence and then delamination from ACP (stage V-b). For the classical nucleation pathway, in stage III, the HA crystals directly nucleate from the ion-rich liquid phase. The HA crystals grow by agglomeration and coalescence (stage IV, bottom).
