Fig. 6. Looming responses of W3 and OFFα ganglion cells depend on VG3 amacrine cells.
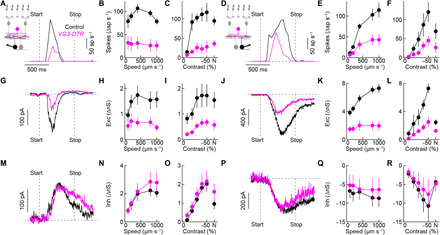
(A to F) Representative traces and summary data of W3 (A to C) and OFFα (D to F) ganglion cell spike responses to looming. The speed for all representative traces in this figure is 800 μm s−1. Across stimulus speeds and contrasts (including luminance-neutral approach motion; N), spike responses of W3 (control: n = 6 cells; VG3-DTR: n = 6 cells; speed: P = 4 × 10−5; contrast: P = 0.0017, bootstrapping) and OFFα (control: n = 4 to 5 cells; VG3-DTR: n = 6 to 8 cells; speed: P = 0.048; contrast: P = 0.047, bootstrapping) ganglion cells were attenuated by VG3 amacrine cell removal. (G to L) Synaptic excitation was reduced by VG3 amacrine cell removal in W3 (G to I; control: n = 5 cells; VG3-DTR: n = 7 to 8 cells; speed: P = 0.0024; contrast: P = 0.0021, bootstrapping) and OFFα (J to L; control: n = 4 cells; VG3-DTR: n = 4 cells; speed: P = 3 × 10−5; contrast: P = 0.0013, bootstrapping) ganglion cells. (M to R) Looming-evoked synaptic inhibition was unaffected by VG3 amacrine cell removal in W3 (M to O; control: n = 5 cells; VG3-DTR: n = 6 to 7 cells; speed: P = 0.77; contrast: P = 0.82, bootstrapping) and OFFα (P to R; control: n = 5 cells; VG3-DTR: n = 4 cells; speed: P = 0.91; contrast: P = 0.83, bootstrapping) ganglion cells. The control data for different looming speeds in this figure are the same as those in Fig. 4. Exc, excitation; Inh, inhibition.
