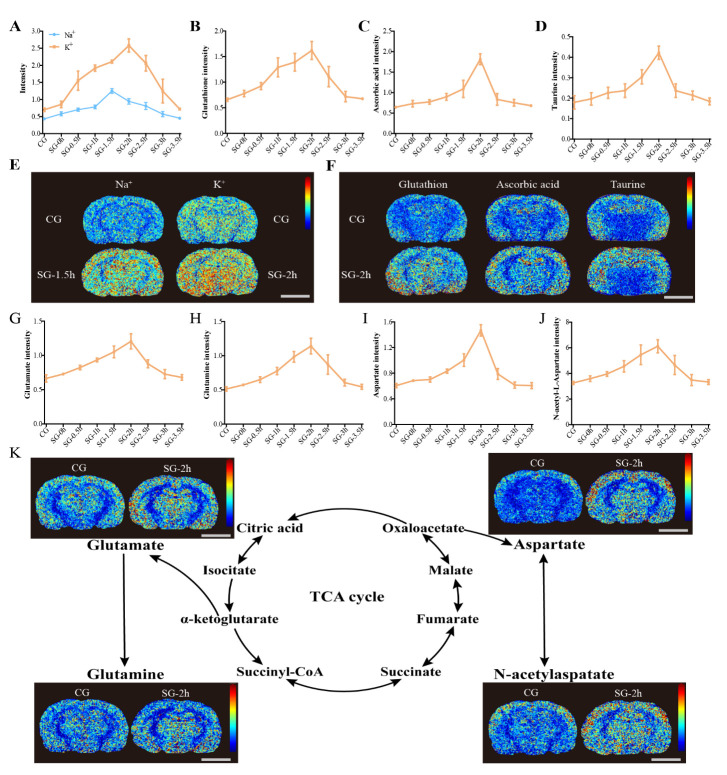
Figure 4.
Dynamic changes in the metabolism of substances in the ECS of the thalamus induced by electrical stimulation. (A-D, G-J) Compared with the CG, electrical stimulation caused dynamic changes in the metabolism of many molecular substances in the rat thalamus, including inorganic ions, antioxidants (glutathione, ascorbic acid, and taurine), glutamate, glutamine, aspartate, and N-acetylaspartate. The most significant changes in the amount of these macromolecules were observed in the SG-2h group. The stimulation-induced metabolic changes were effectively restored after 3 h. (E-F, K) The results from the MSI images showed that the average density of metabolites was significantly increased after electrical stimulation compared with the average density of metabolites in the CG (scale bar, 5 mm). Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Abbreviations: ECS: extracellular space; CG: control group; SG: stimulation group; TCA cycle: tricarboxylic acid cycle; MSI: mass spectrometry imaging.