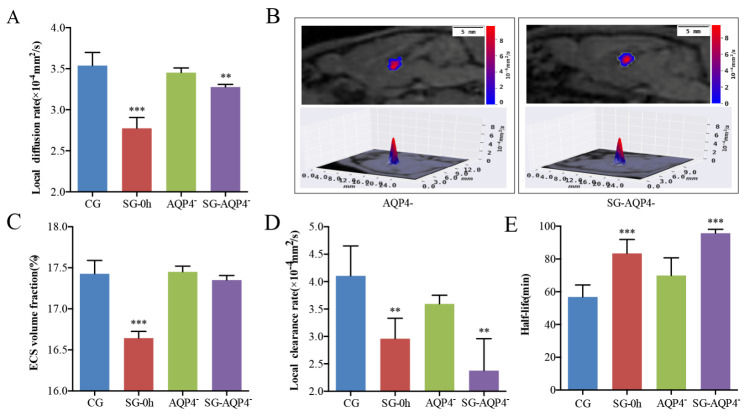
Figure 5.
Effects of electrical stimulation on the diffusion parameters of the ECS structure and ISF drainage in the thalamus of AQP4 knockout rats. (A, C-E) Tracer-based MRI showed that the biophysical parameters of the ECS structure and ISF drainage in the thalamus of the AQP4 knockout rats were similar to those in the thalamus of the CG. Meanwhile, electrical stimulation did not result in significant changes in the α of the thalamus. However, electrical stimulation after AQP4 knockout significantly reduced the DECS and ISF drainage in the thalamus and significantly increased the half-life of ISF, similar to the stimulation group. (B) The contour maps of the DECS-mapping images showed that compared with the AQP4 deficiency group, no significant differences were observed in the patterns and amplitudes of the contour maps of DECS in the AQP4 deficiency with electrical stimulation group (SG-AQP4-) rats. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. Abbreviations: ECS: extracellular space; ISF: interstitial fluid; CG: control group; SG: stimulation group; AQP4-: AQP4-deficient group; SG-AQP4-: stimulation and AQP4 deficiency group; DECS: effective diffusion coefficient of the ECS; α: volume fraction.