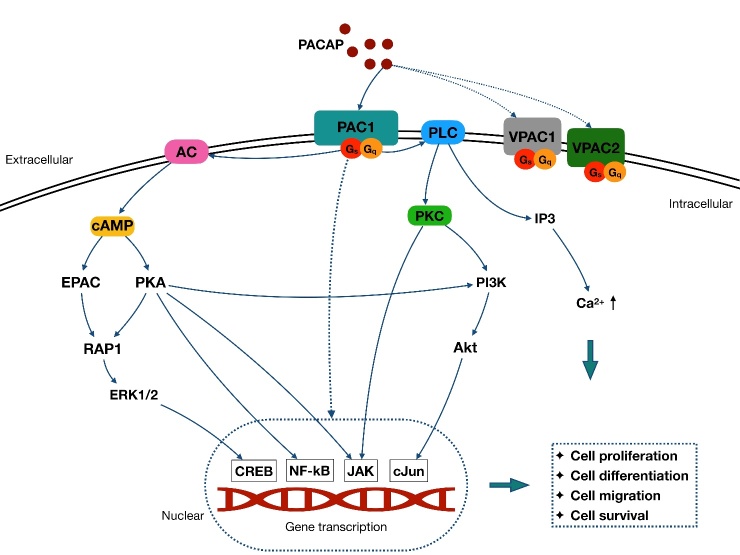
Figure 1.
Schematic pathway of PACAP signaling cascades. PACAP exerts function via activation of three different G-protein coupled receptors: PAC1, VPAC1, and VPAC2. The PAC1 has a 100-fold selectivity for PACAP over VIP, contributing to its role as the main functional receptor of PACAP. Each PACAP receptor is coupled primarily to Gs or Gq, which stimulate AC and PLC activation. In the AC-involved signaling pathway, AC accelerates ATP conversion to cAMP, which then prompts PKA phosphorylation and activation of EPAC pathway. In contrast, activation of PLC boosts the PKC pathway, and the IP3 activation to increase the intracellular Ca2+. Both PLC and AC/cAMP signaling pathways are related to the PACAP function by mediating downstream targets, such as the MAPKs family and the PI3K/Akt pathway. These pathways further mediate cell proliferation, differentiation migration, and survival through several nuclear genes, such as CREB, NF-kB, JAK and cJun. Besides, these downstream signaling pathways also appear to be directly activated by PAC1 and are paralleled with PLC and AC/cAMP pathway in some cells.