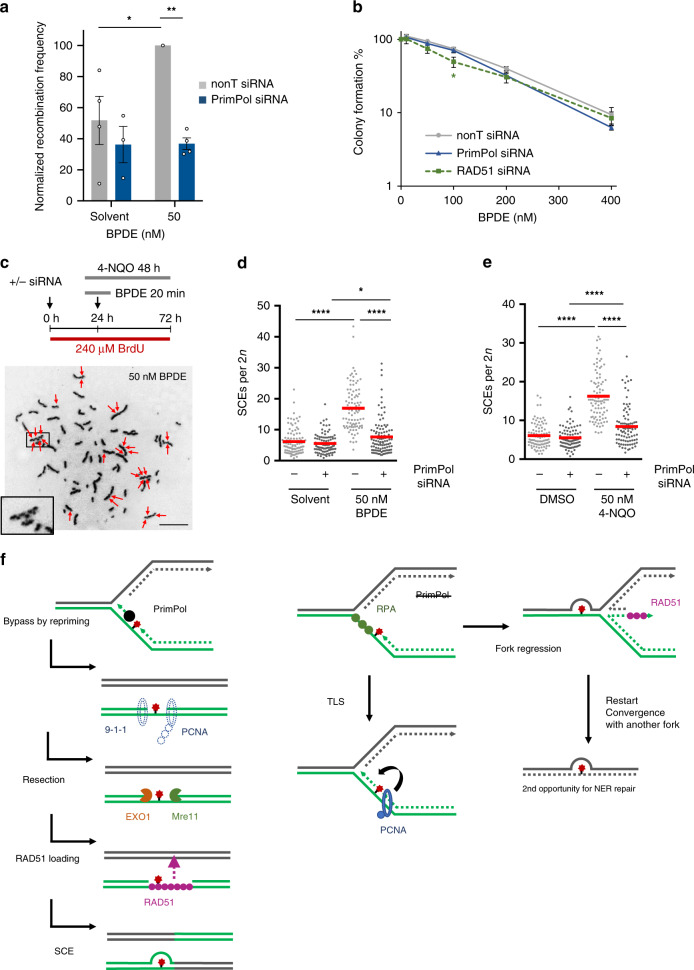
Fig. 6. PrimPol is required for homologous recombination induced by bulky adducts.
a Relative recombination frequencies in SW480SN.3 cells induced by BPDE. Cells were treated with 50 nM BPDE for 20 min in presence of nonT or PrimPol siRNA. n = 4 (PrimPol siRNA solvent n = 3). b Colony survival assay of U2OS cells after 20 min treatment with BPDE at the indicated concentrations in presence of nonT, PrimPol or RAD51 siRNA. n = 4 (RAD51 siRNA n = 3). c Strategy for sister chromatid exchange (SCE) detection and representative picture of metaphase spreads in response to 50 nM BPDE or 4-NQO. Scale bar: 10 μm. d SCE formation in U2OS cells after treatment with 50 nM BPDE or solvent in the presence of nonT or PrimPol siRNA. Lines represent mean. Data from 3 repeats. e SCE formation in U2OS cells after treatment with 50 nM 4-NQO or DMSO in the presence of nonT or PrimPol siRNA. Lines represent mean. Data from 3 repeats. f Model of recombination at bulky DNA adducts. Left: In presence of PrimPol, re-priming creates gaps that are resected for RAD51 foci formation and recombination repair. Potential TLS events at gaps and recombination not resulting in sister chromatid exchanges have been omitted for simplicity. Right: In absence of PrimPol, bulky DNA adducts are either bypassed by TLS or alternatively, stalled forks are stabilized by fork regression and potential rescue upon convergence with another fork. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. The means and SEM (bars) of at least three independent experiments are shown. Asterisks indicate p-values (one-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).