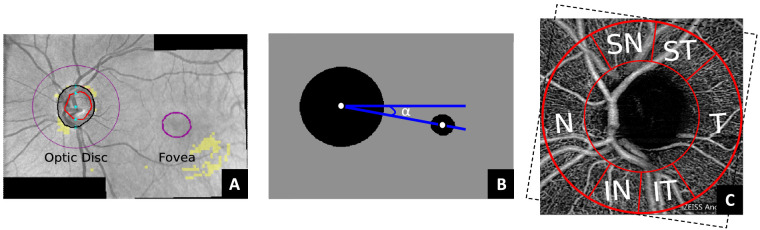
Figure 3.
Example of a Panomap image used to estimate the fovea-disc axis angle (A). The binarization around the optic disc and the fovea, based on the predelineated areas by the device, is followed by the detection of the circles’ centroids and the estimation of the rotation angle () (B). The superimposed mask on the OCTA image at the optic disc (C) is rotated according to . The Garway-Heath sectors nasal (N), inferonasal (IN), inferotemporal (IT), temporal (T), superotemporal (ST), and superonasal (SN) are delineated between the red lines.