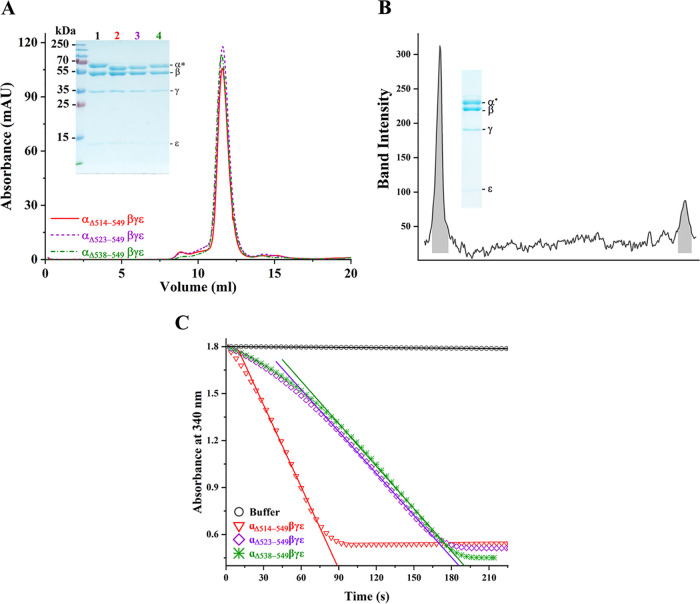
FIG 2.
Characterization of the recombinant MsF1-αΔCTD mutants. (A) Fractions from ion exchange were pooled and subjected to size-exclusion chromatography. The recombinant proteins showed consistency in elution at ∼11.6 ml, and their integrity and constituents were confirmed on a 12% SDS-PAGE gel (inset). The subunits are labeled, where α* refers to subunit α and its mutants β, γ, and ε, which correspond to ∼60, 54 , 35, and 10 kDa, respectively. The corresponding proteins are as labeled: lane 1, MsF1-ATPase; lane 2, MsF1-αΔ514-549βγε; lane 3, MsF1-αΔ523-549βγε; and lane 4, MsF1-αΔ538-549βγε. The purification protocol and 12% SDS-PAGE gel were replicated at least three times, and results represented in the elution diagram and gel remained consistent. (B) Densitometric analysis of the γ to ε ratio of MsF1-αΔ514-549βγε revealed a 1:0.3 ratio, identical to that of the WT enzyme (16) and demonstrating the correct stoichiometric subunit ratio. (C) Recombinant mutants were tested for their ATP hydrolysis rate. The decrease in NADH absorption at 340 nm is plotted against the progressing time. MsF1-αΔ514-549βγε showed a significant increase in ATP hydrolysis (red triangle). On the other hand, MsF1-αΔ523-549βγε (purple diamond) and MsF1-αΔ538-549βγε (green asterisk) showed lesser ATP hydrolysis than MsF1-αΔ514-549βγε. To calculate the specific activity, the initial rate was used (solid lines), and their calculated specific activities and standard error of regression slope (Sb1) were 3.31 ± 0.18, 1.54 ± 0.03, and 1.33 ± 0.01 μmol min−1 (mg of protein)−1.