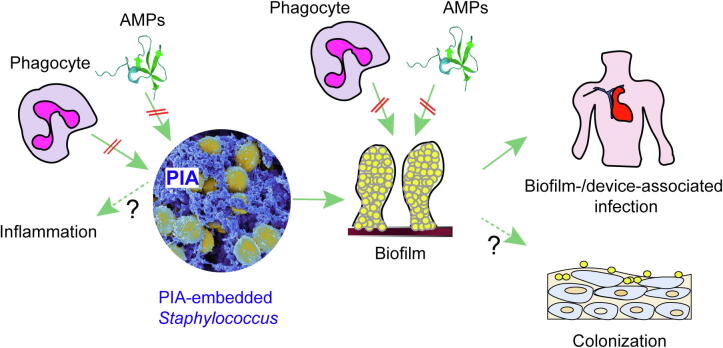
Fig. 3.
Functions of PIA. PIA embeds staphylococcal cells in a dense extracellular matrix network. This network protects the cells from attacks by mechanisms of innate host defense (AMPs, phagocytes). Furthermore, some reports have suggested direct pro-inflammatory functions of PIA. However, most of the biological functions of PIA are mediated by its contribution to biofilm formation. This includes most notably device- and other biofilm-associated infections. Biofilm formation also further contributes to the protection from AMPs and phagocytosis. Finally, PIA may contribute to epithelial colonization under specific conditions.