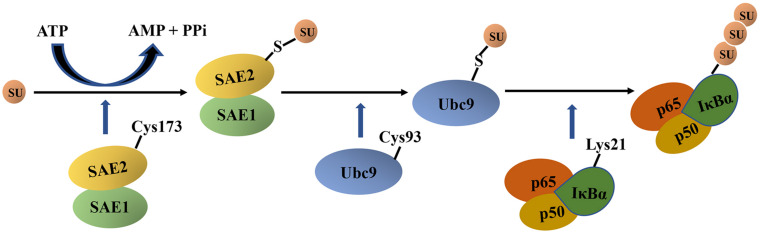
FIGURE 4.
The schematic diagram of IκBα SUMOylation. First, a C-terminal glycine residue of mature SUMO forms a thioester bond with the active site Cys173 in SAE2 in an ATP-dependent manner. Thereafter, SUMO is transferred to the catalytic cysteine residue Cys93 of Ubc9, and Ubc9 directly interacts with IκBα and transfers SUMO to IκBα. Next, the glycine residue at the C terminal of mature SUMO forms a covalent isopeptide bond with the Lys21 side chain in IκBα. IκBα, nuclear factor-kappa B inhibitor alpha; SU, SUMO, small ubiquitin-like modifier; SAE, SUMO-1–activating enzyme; Ubc9, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 9; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; PPi, pyrophosphoric acid.