Fig. 6. Captured alternate SARS-CoV-2 Mpro C-terminal conformations can inform drug discovery.
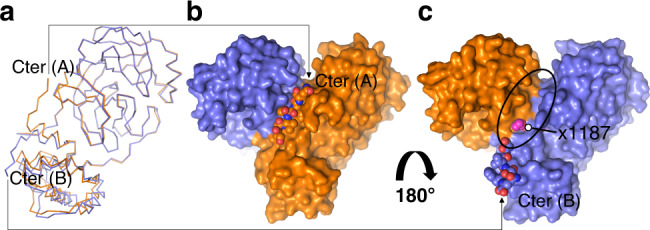
a Superposition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro acyl-enzyme intermediate protomers determined here with chain A and chain B in orange and blue, respectively. The alternate C-terminal orientations—labeled Cter (A) and (B)—observed reveal a druggable pocket at the dimerization interface. Arrows connect to corresponding C-terminal orientation in (b) and (c). b The C-terminus of chain A (orange VdW representations) is packed at and stabilizes the dimerization interface (blue and oranges surfaces), an interaction typical of the mature dimer. c In the acyl-enzyme and product complexes, chain B redirects its C-terminus ~180° (blue VdW representations) as also shown in (a), allowing capture within the active site cleft of a neighboring dimer in the crystal, with the extended peptide binding groove at the dimerization site now exposed (delineated by black ellipse). A recent structure-based fragment screen found several small molecules bound within this region including compound x1187 (magenta spheres; PDB 5RFA).
