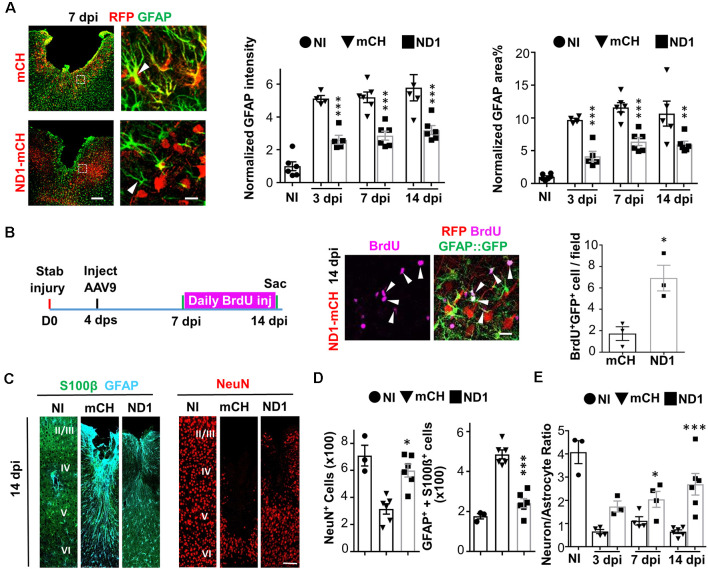
Figure 2.
Rescue of neuron:astrocyte ratio through NeuroD1-mediated in vivo AtN conversion. (A) Astrocytes are not depleted in NeuroD1-converted areas. Control AAV-infected injury areas showed intensive GFAP signals (green) with hypertrophic morphology (top row, 7 dpi). In contrast, NeuroD1-infected injury areas showed significantly reduced GFAP expression, and astrocytic morphology was less reactive (bottom row, arrowhead). Astrocytes (green) persisted in the NeuroD1-converted area (red). Scale bar = 200 μm (low mag, left), and 20 μm (high mag, right). Quantitative analysis revealed a significant reduction of both GFAP intensity and GFAP-covered area in NeuroD1-infected injury areas (right bar graphs). Note that the GFAP signal in the NeuroD1 group was reduced to half of the control group but still higher than non-injured brains, indicating that astrocytes were not depleted after NeuroD1 conversion. n = 4–6 mice per group. Each dot represents one animal. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. (B) Increased proliferation of astrocytes after NeuroD1-mediated cell conversion. BrdU was applied daily in GFAP::GFP mice between 7–14 dpi, a time window of cell conversion, to assess cell proliferation. We detected many proliferating astrocytes that were co-labeled with BrdU (magenta) and GFP (green) in the vicinity of NeuroD1-converted neurons (red). Scale bar = 20 μm. Quantitative analysis revealed a significant increase in the number of proliferating astrocytes (BrdU+/GFP+) in NeuroD1-infected injury areas, compared to the control group. n = 3 mice. *P < 0.05, Student’s t-test. (C) Representative images illustrating astrocytes (S100β, green; GFAP, cyan) and neurons (NeuN, red) in non-injured brains (NI), and stab-injured brains with mCherry control virus infection (mCH) or NeuroD1 virus infection (ND1). Scale bar = 100 μm. (D) Bar graphs illustrating quantitative analyses of the number of NeuN+ neurons, and GFAP+/S100b+ astrocytes among non-injured, mCherry control, and NeuroD1 groups (14 dpi). (E) Rescue of neuron:astrocyte ratio after NeuroD1-mediated AtN conversion. Quantitation of neuron:astrocyte ratio among non-injured, mCherry control, and NeuroD1 groups at 3, 7, and 14 dpi. The neuron:astrocyte ratio was 4:1 in non-injured mouse motor cortex, but significantly decreased to 0.6:1 after stab injury, and then reversed back to 2.6:1 by NeuroD1-mediated AtN conversion. n = 3–6 mice per group. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA plus post hoc Sidak’s test.