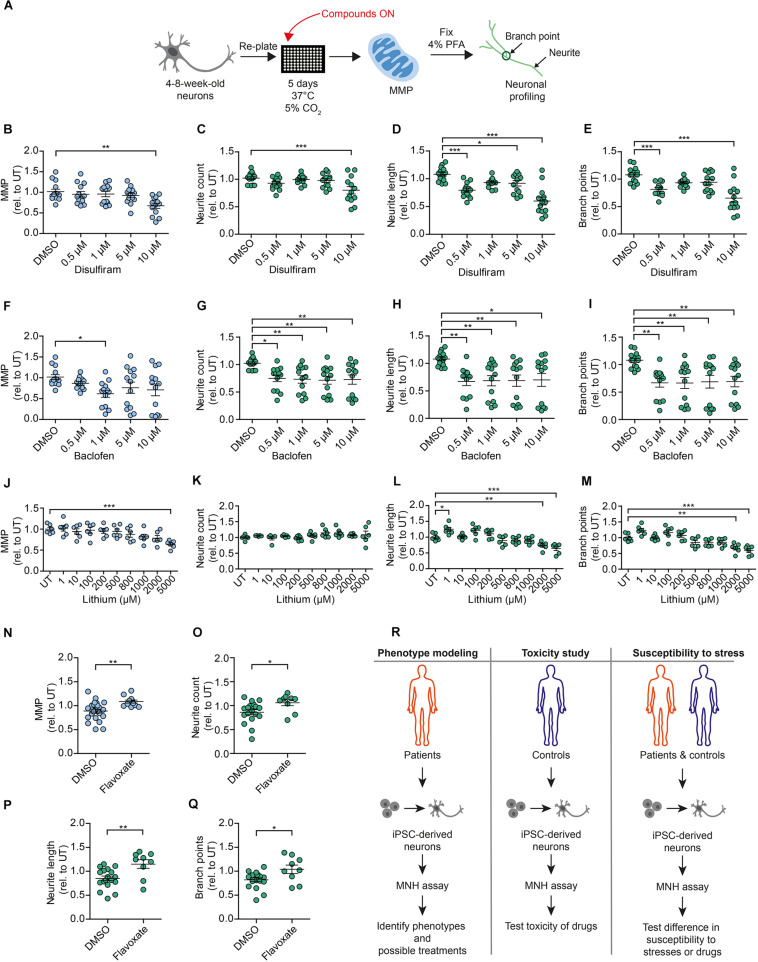
FIGURE 7.
Compounds modulating neuronal toxicity in human DNs. (A) Schematic MNH assay workflow for neuronal toxicity. (B–E) MNH assay-based quantification of MMP (B) and neuronal profiling (C–E) including neurite count (C), neurite length (D), and branch points (E) after ON treatment of 4- to 8-week-old DNs from control iPSCs (XM001) with increasing concentrations of disulfiram (n = 3 independent experiments; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). (F–I) MNH assay-based quantification of MMP (F) and neuronal profiling (G–I) including neurite count (G), neurite length (H), and branch points (I) after ON treatment of 4- to 8-week-old DNs from control iPSCs (XM001) with increasing concentrations of baclofen (n = 3 independent experiments; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). (J–M) MNH assay-based quantification of MMP (J) and neuronal profiling (K–M) including neurite count (K), neurite length (L), and branch points (M) after ON treatment of 4- to 8-week-old DNs from control iPSCs (XM001) with increasing concentrations of lithium (n = 3 independent experiments; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). (N–Q) MNH assay-based quantification of MMP (N) and neuronal profiling (O–Q) including neurite count (O), neurite length (P), and branch points (Q) after ON treatment of 4- to 8-week-old DNs from control iPSCs (XM001) with 1 μM flavoxate (n = 3 independent experiments; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). (R) Schematics of potential applications of the MNH assay.