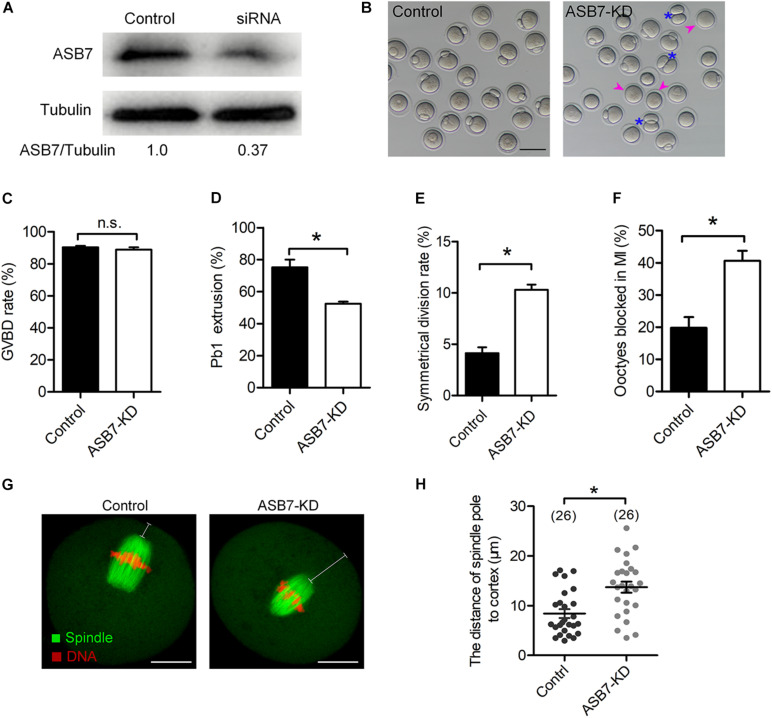
FIGURE 2.
Effects of ASB7 knockdown on maturational progression of mouse oocytes. Fully grown oocytes microinjected with ASB7-siRNAs were arrested at GV stage with milrinone for 20 h. Negative control siRNAs were injected as control. (A) Western blots showing the efficient knockdown of ASB7 after siRNA injection, with tubulin as a loading control (100 oocytes per lane). (B) Phase-contrast images of control and ASB7-siRNA injected oocytes. Pink arrowheads indicate the oocytes that fail to extrude polar bodies and blue asterisks denote oocytes with apparent symmetric division. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C–E) Quantitative analysis of GVBD rate, Pb1 extrusion rate, and symmetrical division rate of control (n = 139) and ASB7-knockdown (n = 152) oocytes. (F) The percentage of oocytes arrested at metaphase I stage after ASB7-siRNA injection. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. (G) Control and ASB7-KD oocytes were sampled after 9.5-h culture and then stained with α-tubulin antibody to visualize spindle (green) and counterstained with PI to visualize chromosome (red). Scale bar: 30 μm. (H) The distance between the spindle pole and plasma membrane was quantified in the control and ASB7-KD oocytes. *p < 0.05 vs controls.