Figure 3.
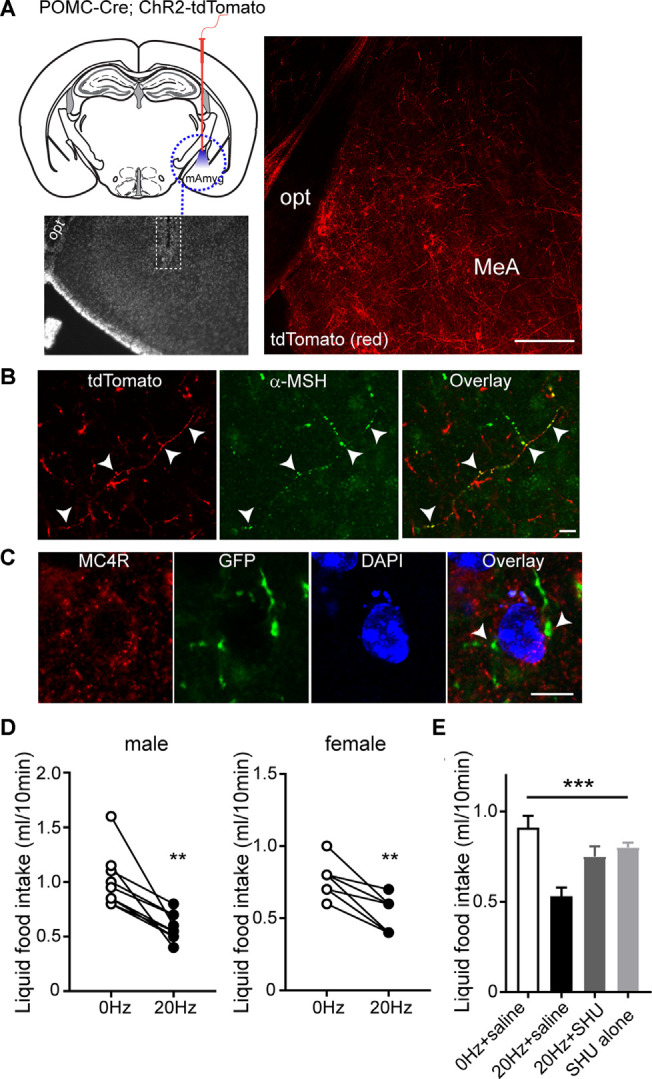
Activating the ARCPOMC→MeA projection leads to an acute reduction in food intake. (A) Schematic drawing of our experimental configurations. A mono fiber-optic cannula was implanted into the MeA of the POMC-Cre; ChR2-tdTomato mice (top panel). The bottom panel shows the implantation site. tdTomato-positive fibers were observed in the MeA of POMC-Cre; ChR2-tdTomato mice. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B) Images of fluorescence confocal microscopy showing that tdTomato-positive fibers were positive for α-MSH in the MeA (white arrowheads). Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Images of fluorescence confocal microscopy showing that MC4R-positive cells receive POMC input from the ARC. GFP-positive fibers and axonal terminals made synaptic contacts with MC4R-positive cells (white arrowheads). Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Pooled data from nine male and seven female mice. Twenty hertz stimulation of the ARCPOMC→MeA pathway significantly reduced liquid food intake (males, 1.0 ± 0.08 ml vs. 0.6 ± 0.04 ml, **p < 0.01, n = 9 mice; females, 0.8 ± 0.05 ml vs. 0.5 ± 0.05 ml, **p < 0.01, n = 7 mice). (E) Plot showing blockade of the effect of optogenetic stimulation of the ARCPOMC→MeA pathway by the MC4R antagonist SHU9119 [1 mg/kg, n = 5 mice, SHU9119 alone, n = 8 mice, Treatment (between groups), F(3,9) = 10.3, ***p < 0.001, 0 Hz + saline vs. 20 Hz + saline, p < 0.001, 20 Hz + saline vs. 20 Hz + SHU9119, p < 0.05, 20 Hz + saline vs. SHU9119 alone, p < 0.01].
