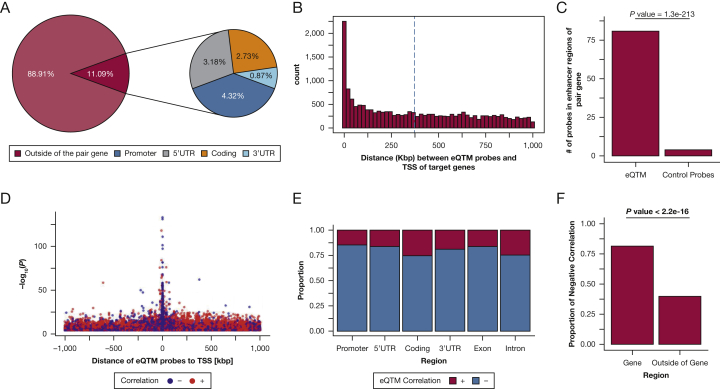
Figure 1.
Characterization and distribution of genomic location of eQTM signals for 16,867 eQTM pairs in nasal epithelium (FDR-P < 0.01). A, Chart depicting whether the probes are located inside of their paired genes. The right chart shows the specific location of probes located inside of their paired genes. B, Distance between eQTM methylation probes and transcription start sites (TSS) of their target genes in kb pairs. C, Number of probes located in enhancer regions of their target genes in lung tissue. eQTM probes vs controls (the same number of eQTM probes). Fisher exact test was conducted to calculate the P value. D, Positive/negative correlation regarding the distance between methylation and TSS and the P value in the eQTM analysis. E, The bar graph shows, within each gene region, the proportion of positive or negative correlation of the eQTM pairs. The correlation is Pearson correlation. F, The proportion of negatively correlated eQTM pairs inside (from promoter to 3’UTRs) and outside genes. The number of eQTM probes inside a gene is 1,871, and the number of the eQTM probes outside of a gene is 14,996. A χ2 test was conducted to examine the association between the region (whether the probe is located in the gene or outside of the gene) and the sign of the correlation. eQTM = expression quantitative trait methylation; FDR-P = false-discovery rate-adjusted P < .01.