Figure 1.
NCKAP1 Disruptive or De Novo Missense Variants and Phenotype Spectrum
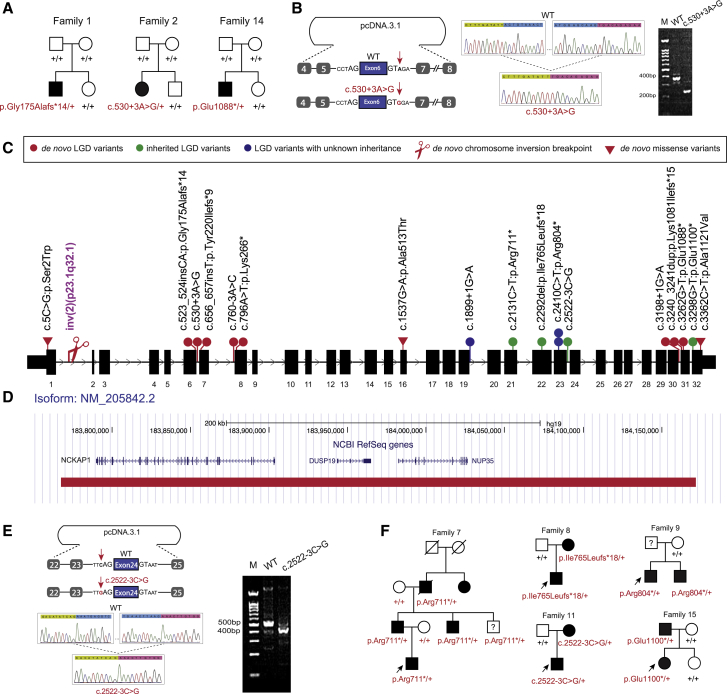
(A) Three families with de novo disruptive (families 1 and 14) or intronic (family 2) variants in SSC cohort.
(B) Minigene assay shows that de novo intronic variant c.530+3A>G impairs normal splicing. Sequence highlighted by green above the Sanger trace is from exon 5. Sequence highlighted by pink is from exon 7.
(C) Distribution of NCKAP1 disruptive and de novo missense variants within the gene.
(D) A de novo deletion (red bar) removed three genes, including NCKAP1, and was identified in family 16.
(E) Minigene assay shows that the intronic variant c.2522−3C>G impairs normal splicing. Sequence highlighted by green above the Sanger trace is from exon 23. Sequence highlighted by pink is from exon 25.
(F) Pedigree plots of families with dominantly transmitted NCKAP1 disruptive variants and neuropsychiatric disorders.