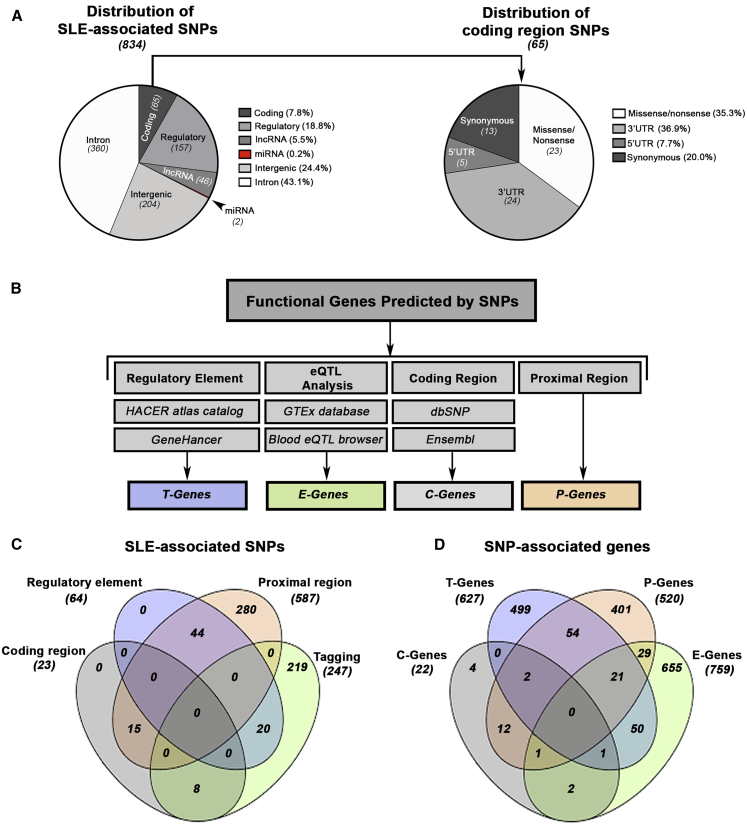
Figure 1.
Mapping the Functional Genes Predicted by SLE-Associated SNPs
(A) Distribution of genomic functional categories for all ancestry-specific non-HLA-associated SLE SNPs (tiers 1–3). Non-coding regions include micro (mi)RNAs, long non-coding (lnc)RNAs, introns, and intergenic regions. Regulatory regions include transcription factor binding sites (TFBS), promoters, enhancers, repressors, promoter flanking regions, and open chromatin. Coding regions were broken down further and include 5′ UTRs, 3′ UTRs, and synonymous and nonsynonymous (missense and nonsense) mutations.
(B) Functional genes predicted by SNPs are derived from four sources including regulatory elements (T-Genes), eQTL analysis (E-Genes), coding regions (C-Genes), and proximal gene-SNP annotation (P-Genes).
(C and D) Venn diagram depicting the overlap of all SLE-associated SNPs (C) and all predicted E-, T-, P-, and C- Genes (D).