Figure 1.
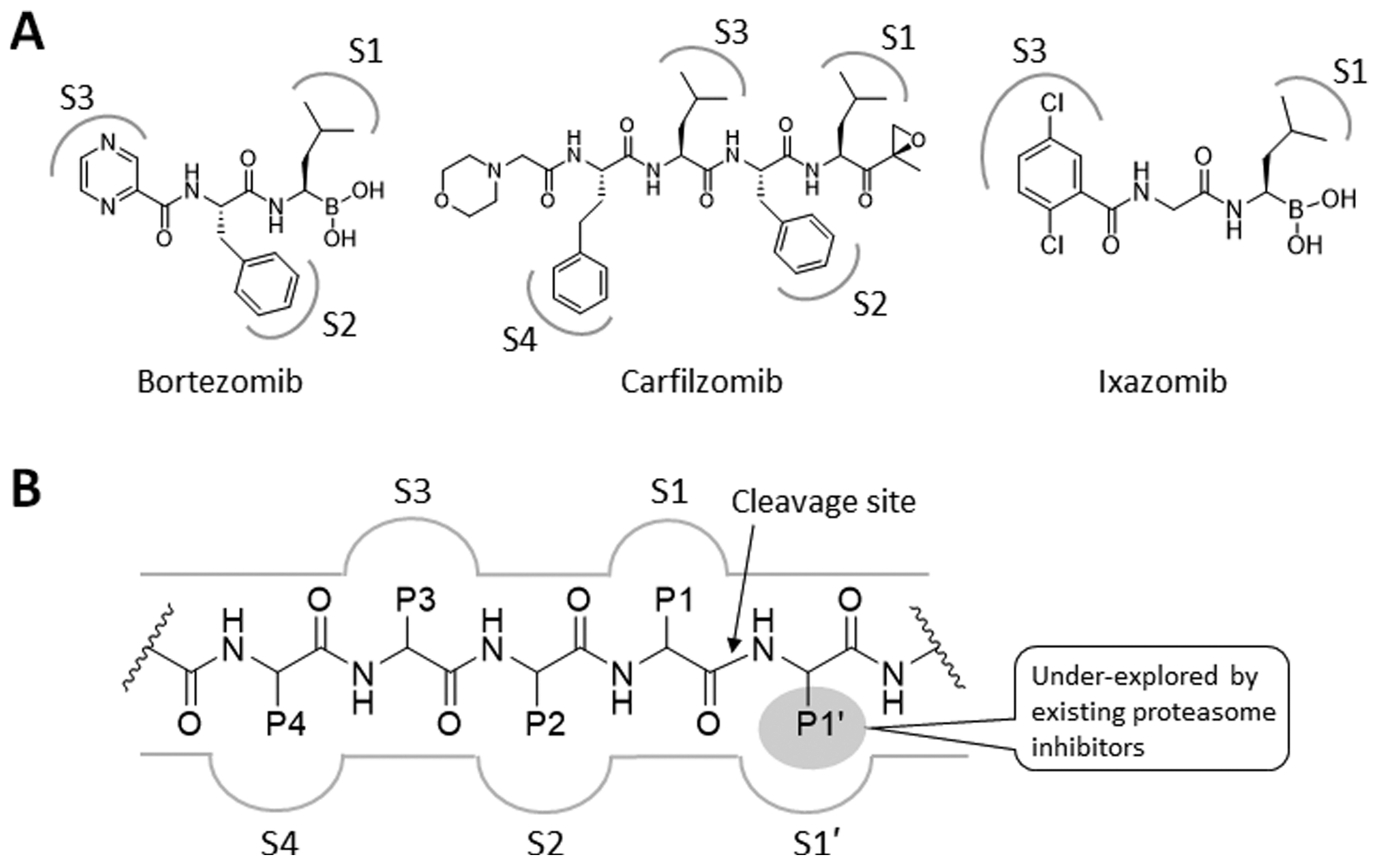
(A) Structures of proteasome inhibitors in clinical use. The gray-colored markings denote the functional groups that are proposed to form favorable interactions with the specificity pockets (S1–4) of a proteasome catalytic subunit. (B) Schematic representation of a prototypical proteasome substrate or substrate-like inhibitor bound to a proteasome catalytic subunit showing the unprimed residues (P1, P2, P3, and P4) located N-terminal to the cleavage site of the proteasome catalytic subunit (shown as an arrow) and the primed P1′ residue located C-terminal to the cleavage site.
