Figure 6.
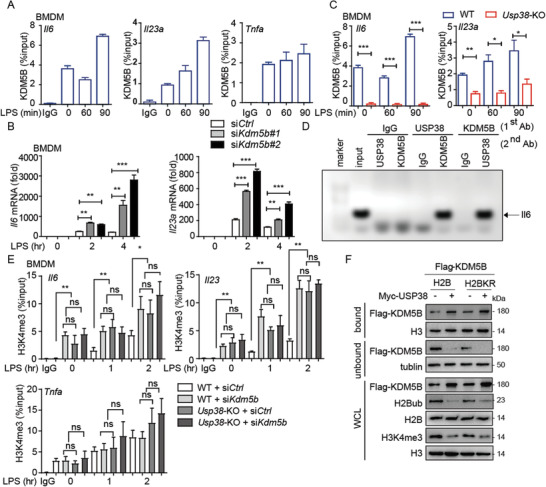
USP38 recruits KDM5B to specifically repress the transcription of Il6 and Il‐23a. A) ChIP‐qPCR of KDM5B at the Il6, Tnfa, and Il23a promoters in BMDMs under LPS treatment for the indicated time points. B) The level of Il6 and Il23a mRNA in Kdm5b‐silenced BMDMs using Kdm5b‐specific siRNAs (siKdm5b#1, siKdm5b#2) under LPS treatment for the indicated time points. C) ChIP‐qPCR of KDM5B at the Il6 and Il23a promoters in wild‐type (WT) or Usp38‐knockout (KO) BMDMs under LPS treatment for the indicated time points. D) Re‐ChIP‐PCR assay of the USP38‐KDM5B interaction at Il6 promoter in BMDMs after LPS stimulation for 2 h. First‐round ChIP (first antibody, Ab) against USP38, KDM5B, or IgG. Eluted samples were re‐ChIPed with the indicated second antibodies. Lane 2 was input. E) ChIP‐qPCR of H3K4me3 at the Il6 and Il23a promoters in WT or Usp38‐KO BMDMs with Kdm5b‐specific siRNA or control siRNA under LPS treatment for the indicated time points; results are presented relative to those of 1% input DNA. F) Immunoblot analysis of KDM5B, H2Bub/H2B, and H3K4me3/H3 in chromatin bound and unbound components of 293T cells with overexpression of Myc‐empty vector (EV), Myc‐USP38, or Myc‐USP38 CAHA mutant along with Flag‐H2B or Flag‐H2BK120R mutant. Data in (A)–(C) and (E) are presented as the means ± SEM of at least three biological experiments. Data in (D) and (F) are representative of three independent biological experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns, no significant difference, versus the WT or control group with the same treatment (Student's t‐test).
