FIGURE 4.
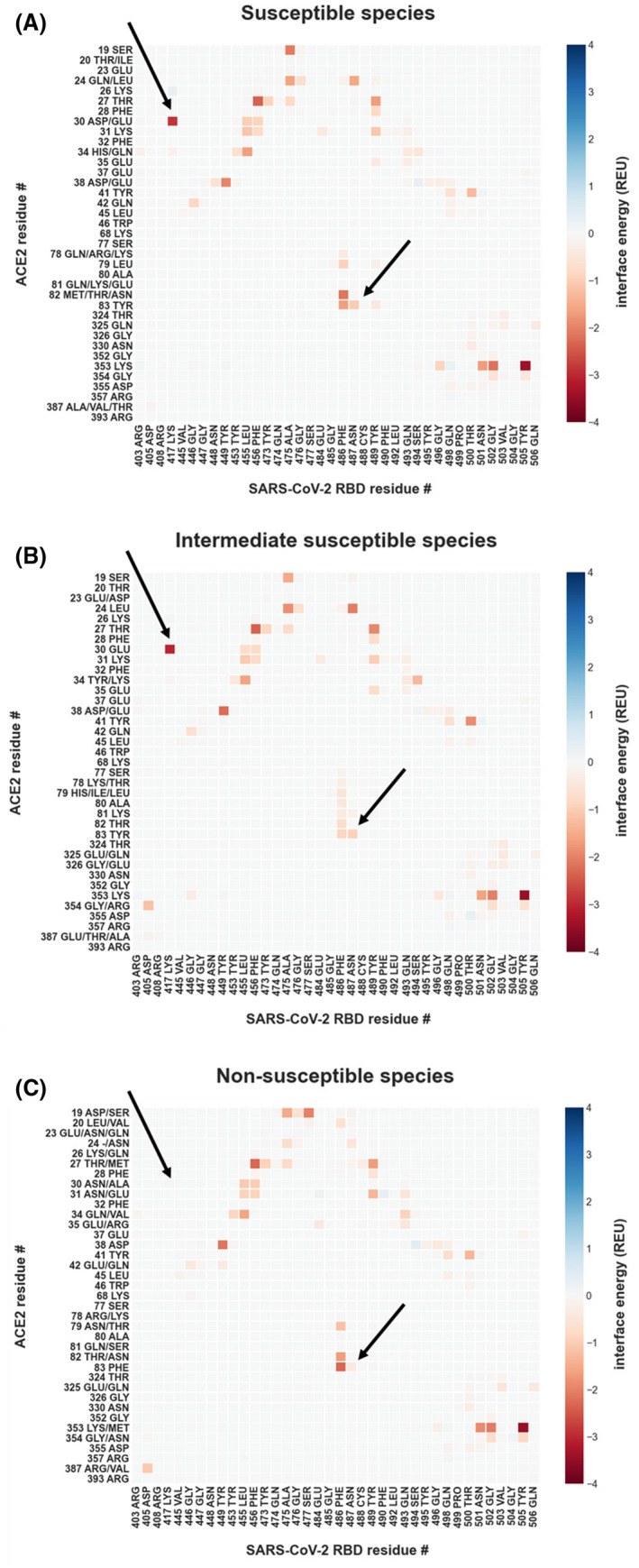
Energetic modeling of residue‐residue interactions identifies a link between ACE2 D30 and Y83 and SARS‐CoV‐2 susceptibility. Residue‐residue interactions are calculated with Rosetta, using the co‐crystal structure of the human ACE2 in complex with the SARS‐CoV‐2‐RBD (PDB: 6LZG and 6M0J) after backbone‐constrained relaxation for all interactions greater than 0.05 Rosetta Energy Units (REU) or smaller than −0.05 REU. Interactions are presented as the mean for all included samples. Residues depicted on the y‐axis are all observed amino acid identities for the particular position in its susceptibility group. (A) Per‐residue interactions for (A) susceptible species (human, cat, lion, tiger, hamster, and rhesus macaque), (B) intermediate susceptibility species (pig, dog, and ferret), and (C) non‐susceptible species (duck, mouse, and chicken). The arrows point to interactions that are not observed in non‐susceptible species
