Figure 1.
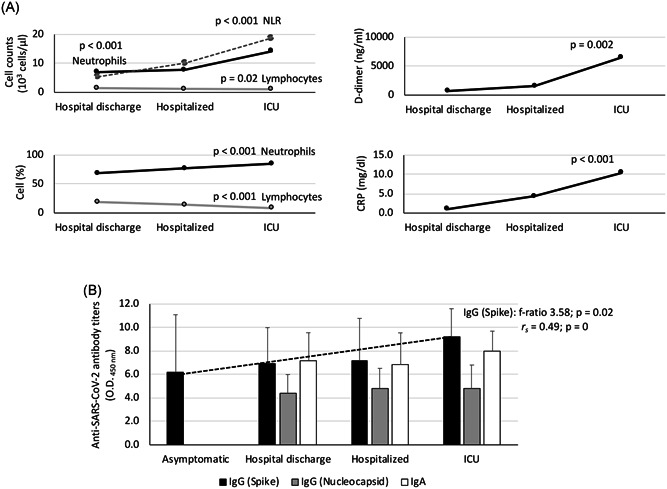
Laboratory tests in COVID‐19 patients. A, Cellular and biochemical indicators of systemic inflammation included neutrophils (cell counts and percent), lymphocytes (cell counts and percent), NLR, D‐dimer and CRP levels (Table 1). B, Serum anti‐SARS‐CoV‐2 IgA, IgG (spike) and IgG (nucleocapsid) antibody levels were determined by ELISA. The patients were grouped as asymptomatic (n = 10), hospital discharge (n = 27), hospitalized (n = 29) and ICU (n = 25). The results were compared between different groups by one‐way ANOVA test (p < .05). A Spearman rho (r s) correlation analysis (p < .05) was conducted between anti‐Spike IgG antibody titers and disease severity (2 = asymptomatic, 3 = hospital discharge, 4 = hospitalized, 5 = ICU). ANOVA, analysis of variance; COVID‐19, coronavirus disease 2019; CRP, C‐reactive protein; ELISA, enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay; ICU, intensive care unit; IgA, immunoglobulin A; NLR, neutrophil‐lymphocyte count ratio; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
