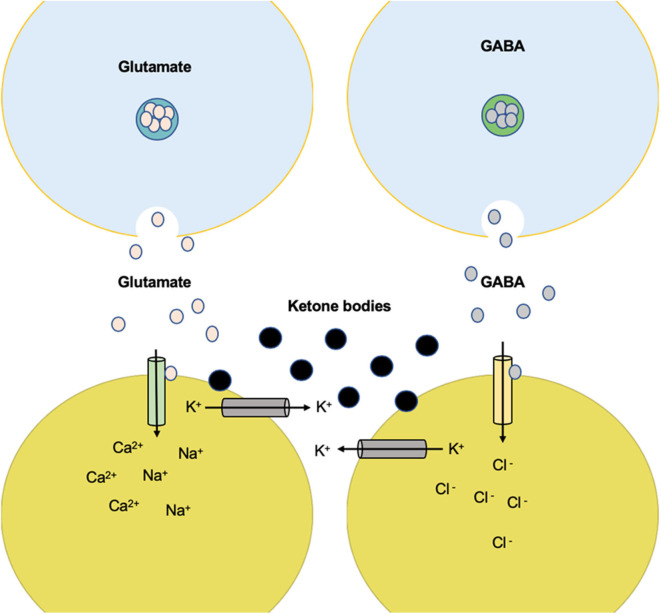
Figure 4.
Anticonvulsant effect of K+ channel-mediated ketone body metabolism. Ketone body metabolism increases overall ATP but reduces glycolysis and glycolytic ATP synthesis. The reduction of ATP near the plasma membrane can disinhibit the KATP channels and therefore reduce electrical activity. High electrical activity (as in a seizure) increases Na+ input and ATP utilization near the plasma membrane. This produces negative changes in activity through the KATP channels. The set point at which this negative feedback safety mechanism is activated is determined by the level of glycolytic ATP synthesis.