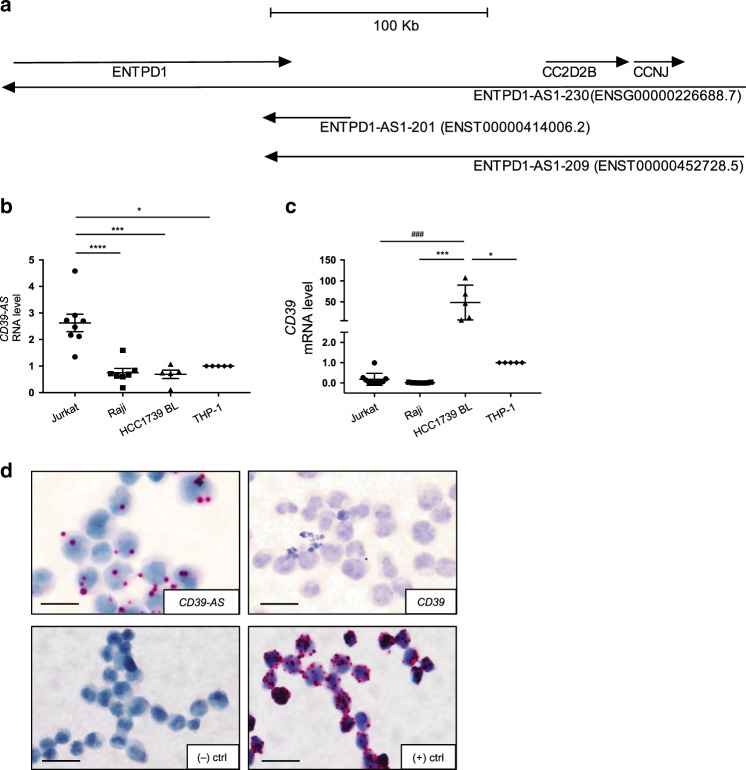
Fig. 1. CD39-AS RNA is located at the 3′ end of the human CD39 gene and regulates CD39 mRNA levels.
a Graphical representation of the 10q24.1 human locus, including CD39/ENTPD1, CC2D2B, and CCNJ genes, ENTPD1-AS1-230 (ENSG00000226688.7) long transcript antisense RNA variant, and two ENTPD1/CD39-AS splice variants. The two ENTPD1-AS1-209 (ENST00000452728.5) and ENTPD1-AS1-201 (ENST00000414006.2) splice variants, predicted by Ensembl and UCSC genome browsers, were experimentally confirmed by qRT-PCR analysis. These were both transcribed from the 3′ end of the human ENTPD1/CD39 gene. b, c Mean ± SEM CD39-AS RNA and CD39 mRNA levels in Jurkat (n = 8 replicates), Raji (n = 7 replicates), HCC1739BL (n = 5 replicates), and THP-1 (n = 5 replicates) cell lines. Because of high CD39-AS RNA and concomitantly low CD39 mRNA levels, Jurkat cells were used for all subsequent experiments as positive control for antisense RNA expression. BaseScope and RNAScope chromogenic assays were used to detect CD39-AS RNA and CD39 mRNA transcripts in cytospins of Jurkat cells. d Representative images of Jurkat cells stained with CD39-AS BaseScope, CD39 RNAScope, and negative and positive control staining is shown (magnification ×40, scale bar: 25 μM). A representative of three independent experiments is shown. Comparisons in b, c were made using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (b: *P = 0.013; ***P = 0.0002; ****P ≤ 0.0001; c: *P = 0.013; ***P = 0.0004; ###P = 0.0002).