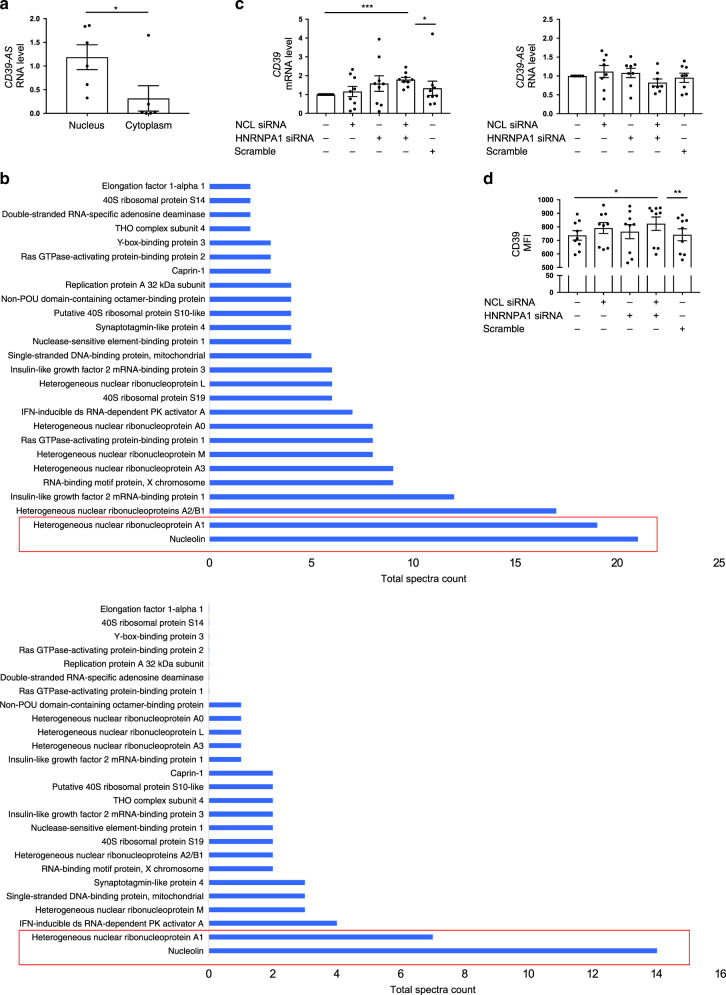
Fig. 5. CD39-AS RNA is predominantly localized in the nucleus and binds to nucleolin and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1.
Nuclear and cytosolic subcellular fractions were obtained from Jurkat cells and tested for CD39-AS RNA expression. a Mean ± SEM CD39-AS RNA levels in n = 6 Jurkat cell replicates (*P = 0.042 using two-sided unpaired t test). In order to identify the potential binding proteins to the antisense RNA, RNA pulldown was carried out, followed by mass spectrometry. b Proteins identified by mass spectrometry as binders of ENST00000452728.5 and ENST00000414006.2 antisense splice variants are shown. Nucleolin (NCL) and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (HNRNPA1) were the proteins showing the highest number of total spectra counts for both splice variants. c, d Mean ± SEM CD39 mRNA and CD39-AS RNA levels and MFI of Jurkat cells in the absence or presence of siRNA specific to NCL, HNRNPA1, NCL plus HNRNPA1, or scramble. Exposure of Jurkat cells to NCL and HNRNPA1 siRNAs results in increased CD39 mRNA levels and MFI (CD39 mRNA n = 9 replicates; CD39 AS RNA n = 8 replicates; CD39 MFI n = 8 replicates) (c ***P = 0.0002, *P = 0.04; d *P = 0.015, **P = 0.009 using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test).