Figure 5 |. Synaptic connections of auditory neural pathways.
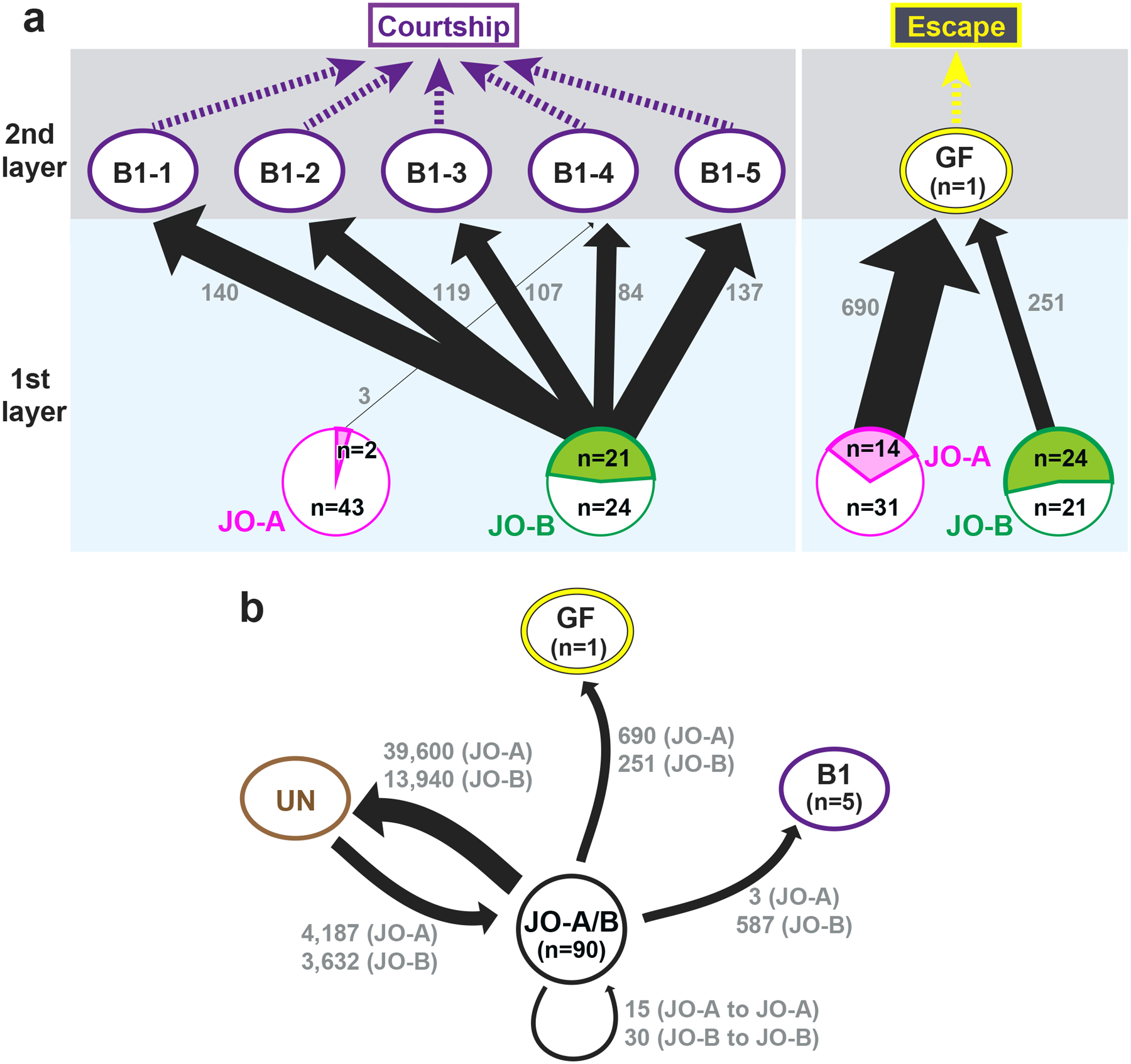
(a) Connection diagram between JO neurons and the two pathways. The AMMC-B1 (B1) pathway, which feeds into the courtship-song relay pathway, receives many synaptic inputs from JO-B neurons and a few inputs from JO-A neurons (left). The GF pathway, which feeds into an escape pathway, receives many synaptic inputs from both JO-A and JO-B neurons (right). The arrow width reflects the number of synaptic connections. The number at each arrow (gray) indicates the number of synapses from JO neurons to each second-order neuron (AMMC-B1 or GF neuron). The magenta and green areas in JO-A and JO-B circles (bottom) represent the ratio of JO-A and JO-B neurons, respectively, that feed into AMMC-B1 (left) and GF neurons (right). The white area in each circle represents JO-A and JO-B neurons that have no output synapses to AMMC-B1 and GF neurons. “n” in the circle indicates the number of traced JO neurons that are connected (in magenta or green area) or not connected (in white area) to AMMC-B1 (left) and GF neurons (right). (b) Synaptic contacts between JO neurons and other neurons. JO-A and JO-B neuron axons receive many synaptic inputs from unidentified neurons (UN) but not from GF and AMMC-B1 neurons. There are no synaptic contacts between JO-A and JO-B neurons. The number at each arrow shown in gray color indicates the number of synapses.
