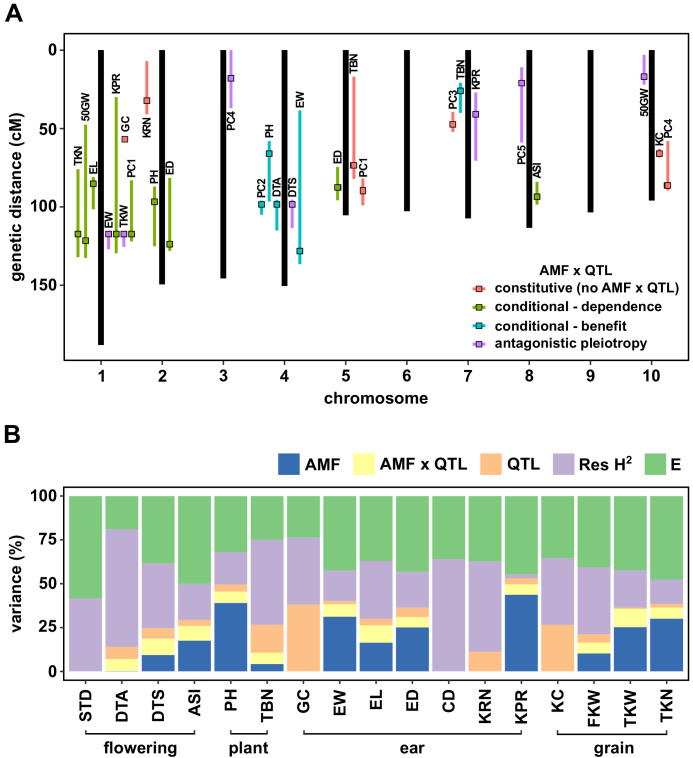
Figure 3. QTL x AMF effects contribute significantly to variation in host response.
(A) Genomic position of QTL identified in this study. Boxes indicate the position of the peak marker. Bars represent the drop-1 LOD interval. Colors denote patterns of AMF × QTL interaction as described in the text. (B) The contribution of different components to phenotypic variance in different plant traits among AMF-S and AMF-R families. Total genetic variance was estimated based on differences between experimental blocks and partitioned into variation explained by the additive effect of AMF, the additional variation explained by interactive QTL and QTL × AMF interaction (QTL × AMF), the additional variation explained by additive QTL (QTL) and residual genetic variation (Res H2). The balance of the phenotypic variance was assigned to the environment (E). Traits codes as in Table 1.