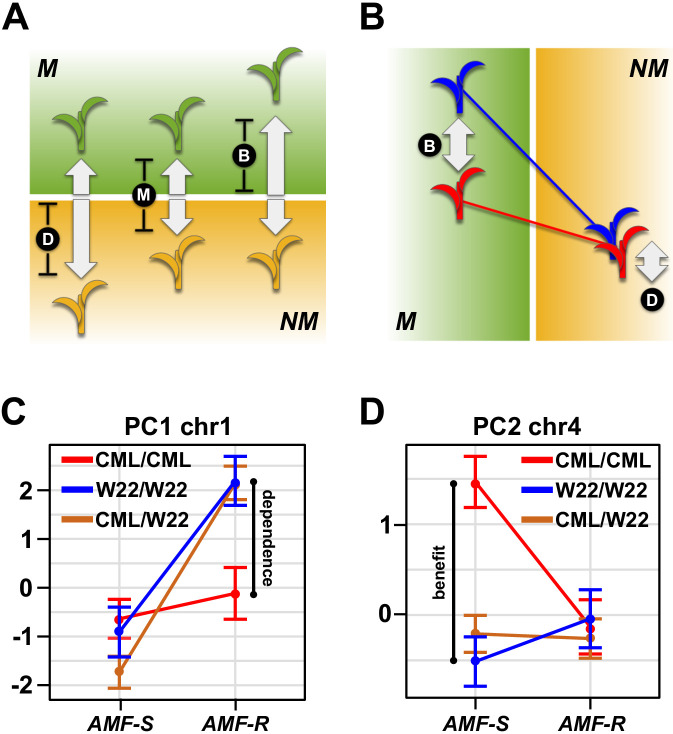
Figure 4. Mycorrhiza response confounds benefit and dependence.
(A) Host response (R) is the difference in trait value between mycorrhizal (M; green) and non-mycorrhizal (NM, yellow) plants. Increased response can result from either greater dependence (D; poorer performance of NM plants) or greater benefit (B; greater performance of M plants). (B), QTL × AMF effects underlying variation in response reveal the balance of benefit and dependence. In this theoretical example, the effect is conditional on mycorrhizal colonization, reflecting a difference in benefit more than dependence. (C, D) Effect plots for major QTL associated with PC1 and PC2, respectively. Effect of the homozygous CML312 (red), homozygous W22 (blue), or heterozygous (brown) genotypes in AMF-S and AMF-R families. The PC1 QTL is conditional on AMF-R, indicating a difference in dependence. The PC2 QTL is conditional on AMF-S, indicating a difference in benefit.