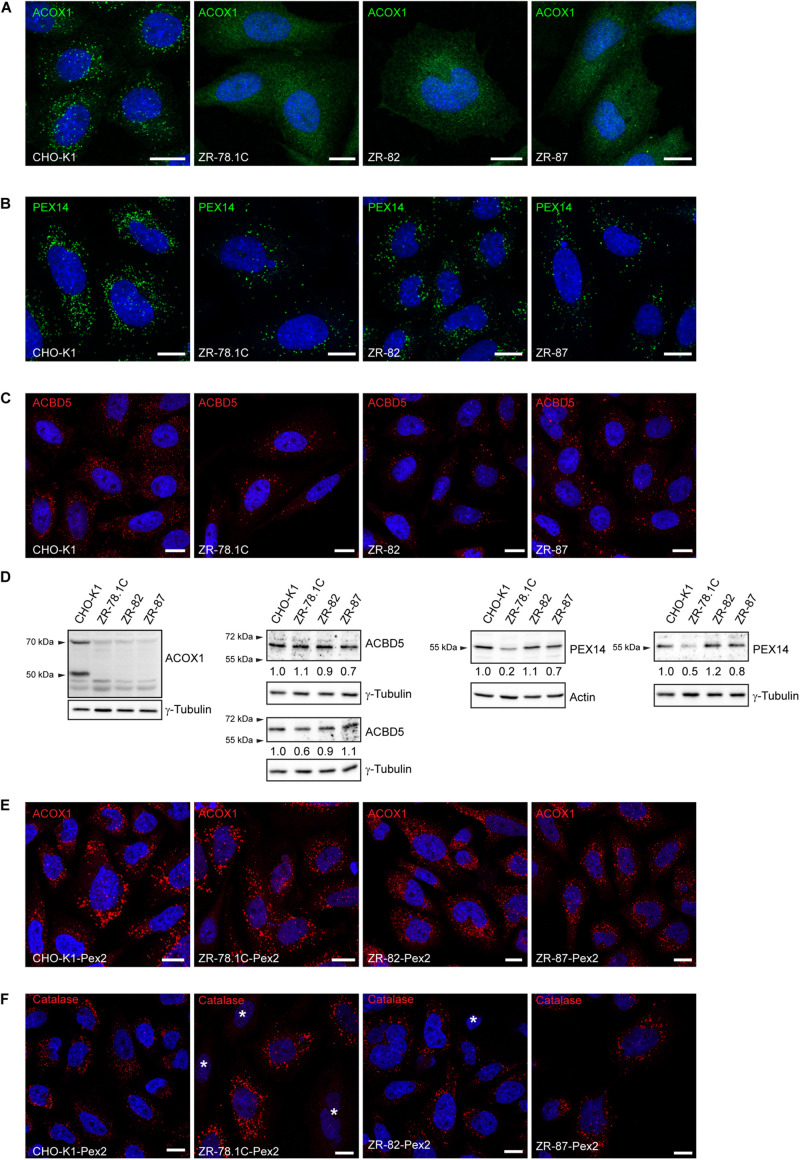
FIGURE 2.
Peroxisome-deficient CHO cells contain peroxisome membraneghosts. (A) Peroxisomes were detected with an antibody against the peroxisomal matrix protein ACOX1. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Note the cytoplasmic localization of Acox1 in the peroxisome-deficient ZR-78.1C, ZR-82, and ZR-87 cells. (B) Peroxisomes were detected with an antibody against the peroxisomal membrane protein PEX14. Note the presence of peroxisome membrane ghosts in peroxisome-deficient CHO cells. The number of peroxisome membrane ghosts in peroxisome-deficient CHO cells is significantly lower than the number of peroxisomes in CHO-K1 cells. (C) Peroxisomes were visualized with an antibody against the peroxisomal tail-anchored protein ACBD5. Note that ACBD5 localizes to peroxisome membrane ghosts in peroxisome-deficient CHO cells. (D) Immunoblots of total cell lysates with antibodies against peroxisomal matrix and membrane proteins. Numbers at the bottom of the blots indicate the fold change in protein levels in peroxisome-deficient cells relative to that in CHO-K1 cells, which were arbitrarily defined as 1. (E,F) Functional peroxisomes are restored in peroxisome-deficient CHO mutants (ZR-78.1C, ZR-82, ZR-87) upon complementation with rat Pex2 cDNA. Cells were immunostained with antibodies against the peroxisomal matrix proteins ACOX1 (E) and catalase (F). The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). An asterisk indicates non-transfected cells without import-competent peroxisomes. The scale bars represent 10 μm.