Figure 2: Human disease subjects vary from healthy controls in critical microbiota-associated variables that confound microbiota analyses.
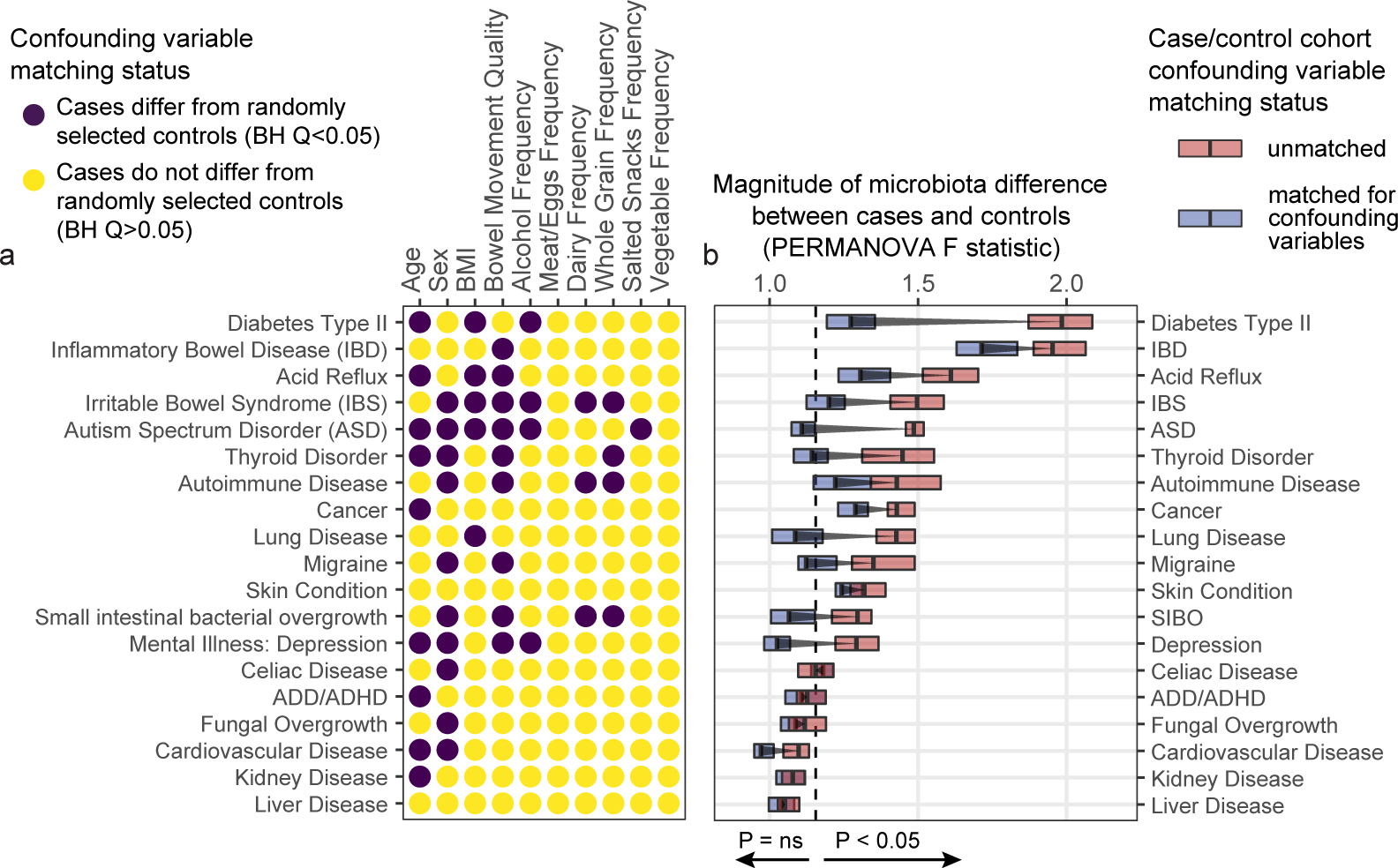
A) Shown in purple are variables that differ in disease cases versus randomly selected location-paired control subjects (Benjamini-Hochberg Q value < 0.05). For continuous variable comparisons (age, BMI) a two-sided Mann-Whitney U test was performed, while for remaining categorical variable comparisons a Fisher’s exact test was performed. B) Shown are differences between beta diversity-based F statistics of unmatched, location-paired disease case-control cohorts and those of fully matched case-control cohorts. Analyses were augmented using a bootstrapping control cohort re-selection method to assess dispersion of microbiota community differences (described in Methods). Red boxes represent interquartile ranges in F statistics from 25 randomly selected location-paired unmatched cohorts, while blue boxes represent interquartile ranges in F statistic from 25 randomly selected cohorts for which controls were selected that matched cases for all microbiota-associated host variables that differed between cases and controls shown in (A). Center lines within boxes represent median F statistic values.
