Extended Data Fig. 1 |. Electron microscopic imaging of VZV particles.
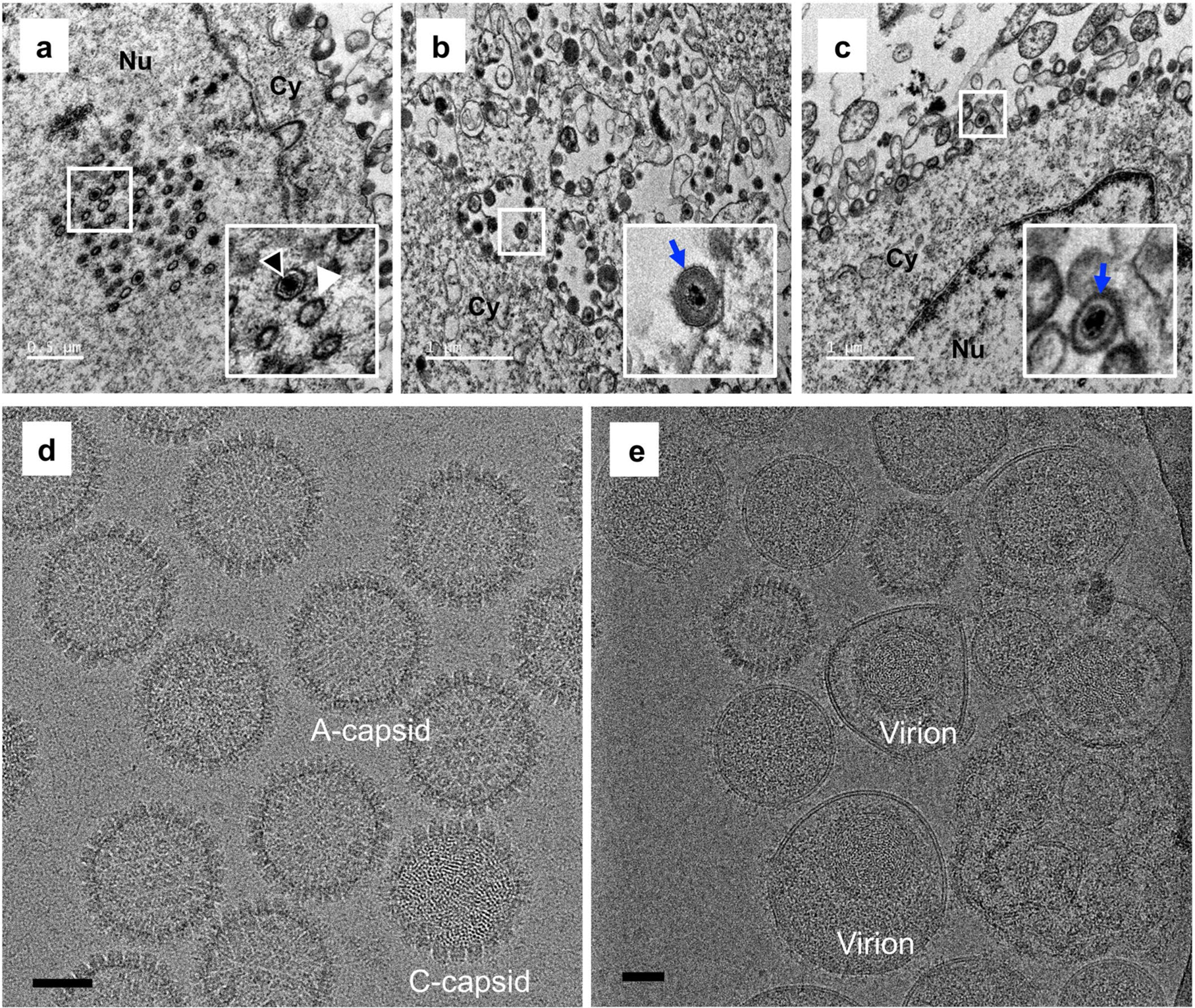
a–c, Representative electron microscopic images of VZV-infected ARPE-19 cells recorded at 3 days post-infection (dpi) using a Tecnai G2 Spirit transmission electron microscope. Panel a shows VZV nucleocapsids in the nucleus of an infected cell. Intact capsids are indicated by black arrow heads, and capsids without an electron-dense core are indicated by white arrow heads. Panel b,c show enveloped viral particles (blue arrows) within cytoplasmic vacuoles and on the surface of infected cells, respectively. Insets show enlarged images of the boxed areas. Experiments were performed two times independently with similar results. Nu and Cy indicate the nucleus and cytoplasm, respectively. Scale bars in a–c denote 0.5 μm, 1 μm and 1 μm, respectively. d, Purified VZV naked particles were recorded using a Gatan K2 Summit direct electron detector, showing two types of particles in our sample preparation: DNA-containing C-capsid and DNA-devoid A-capsid. Experiments were performed two times independently with similar results. e, Purified VZV virions were recorded using a Falcon3 direct electron detector. Experiments were performed two times independently with similar results. Scale bars in d,e denote 50nm.
