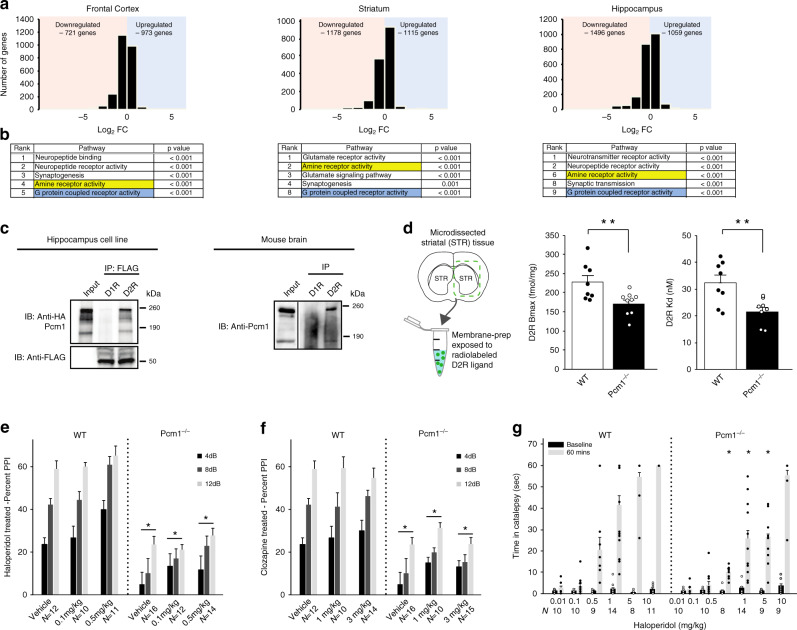
Fig. 4. Altered dopaminergic signaling components in Pcm1−/− mice.
a mRNA sequencing from three brain regions in WT and Pcm1−/− adults (N = 3/genotype, 3 regions per subject): total number of genes up-regulated and down-regulated are plotted on a log2FC scale. b Gene set enrichment analysis revealed amine and G protein coupled receptor activity pathways were altered across the three brain regions. c Immunoprecipitations for D1R (dopamine D1 receptor) and D2R (dopamine D2 receptor), followed by western blot for Pcm1 in mouse hippocampal cell lines and mouse brain homogenates. d Striatal (STR) membrane preparations from WT and mutant brains were dissected, membranes were isolated, and binding studies were instituted with the radiolabeled D2R antagonist [3H]-raclopride. Both the D2R Bmax and Kd levels were reduced significantly in samples from mutant mice (N = 8 WT, N = 9 Pcm1−/−; p = 0.01 (Bmax); p = 0.004 (Kd)). ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni adjustment. e, f PPI responses from P90-120 WT and Pcm1−/− mice indicate that mutants fail to respond at WT levels upon exposure to different doses of haloperidol (e) (Overall genotype effect, p = 0.001 PPI x genotype) or clozapine (f) (Overall genotype effect, p = 0.001). g Catalepsy in WT and Pcm1−/− mice after 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 mg kg−1 haloperidol ((RMANOVA Pre/Post × Treatment × Genotype, p = 0.002)). e–g N shown in graph, analyzed as RMANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni adjustment. Data shown as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, WT vs. Pcm1−/−. Source data and detailed statistical information are provided as a Source Data File. RNAseq data has been made publicly available. Illustrations are original.